- File Handling in Java
- Java
- Streams in Java
- 1. Input Stream:
- Creating an InputStream
- Methods of InputStream
- 2. Output Stream:
- Creating an OutputStream
- Methods of OutputStream
- 1. Byte Stream:
- 2. Character Stream:
- Java File Class Methods
- File operations in Java
- File Handling in Java
- Types of Operation
- How does file Handling work?
- File Handling Methods
- Examples of File Handling in Java
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
File Handling in Java
In Java, with the help of File Class, we can work with files. This File Class is inside the java.io package. The File class can be used by creating an object of the class and then specifying the name of the file.
Why File Handling is Required?
- File Handling is an integral part of any programming language as file handling enables us to store the output of any particular program in a file and allows us to perform certain operations on it.
- In simple words, file handling means reading and writing data to a file.
Java
In Java, the concept Stream is used in order to perform I/O operations on a file. So at first, let us get acquainted with a concept known as Stream in Java.
Streams in Java
- In Java, a sequence of data is known as a stream.
- This concept is used to perform I/O operations on a file.
- There are two types of streams :
1. Input Stream:
The Java InputStream class is the superclass of all input streams. The input stream is used to read data from numerous input devices like the keyboard, network, etc. InputStream is an abstract class, and because of this, it is not useful by itself. However, its subclasses are used to read data.
There are several subclasses of the InputStream class, which are as follows:
- AudioInputStream
- ByteArrayInputStream
- FileInputStream
- FilterInputStream
- StringBufferInputStream
- ObjectInputStream
Creating an InputStream
// Creating an InputStream InputStream obj = new FileInputStream();
Here, an input stream is created using FileInputStream.
Note: We can create an input stream from other subclasses as well as InputStream.
Methods of InputStream
| S No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | read() | Reads one byte of data from the input stream. |
| 2 | read(byte[] array)() | Reads byte from the stream and stores that byte in the specified array. |
| 3 | mark() | It marks the position in the input stream until the data has been read. |
| 4 | available() | Returns the number of bytes available in the input stream. |
| 5 | markSupported() | It checks if the mark() method and the reset() method is supported in the stream. |
| 6 | reset() | Returns the control to the point where the mark was set inside the stream. |
| 7 | skips() | Skips and removes a particular number of bytes from the input stream. |
| 8 | close() | Closes the input stream. |
2. Output Stream:
The output stream is used to write data to numerous output devices like the monitor, file, etc. OutputStream is an abstract superclass that represents an output stream. OutputStream is an abstract class and because of this, it is not useful by itself. However, its subclasses are used to write data.
There are several subclasses of the OutputStream class which are as follows:
- ByteArrayOutputStream
- FileOutputStream
- StringBufferOutputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
- DataOutputStream
- PrintStream
Creating an OutputStream
// Creating an OutputStream OutputStream obj = new FileOutputStream();
Here, an output stream is created using FileOutputStream.
Note: We can create an output stream from other subclasses as well as OutputStream.
Methods of OutputStream
| S. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | write() | Writes the specified byte to the output stream. |
| 2. | write(byte[] array) | Writes the bytes which are inside a specific array to the output stream. |
| 3. | close() | Closes the output stream. |
| 4. | flush() | Forces to write all the data present in an output stream to the destination. |
Based on the data type, there are two types of streams :
1. Byte Stream:
This stream is used to read or write byte data. The byte stream is again subdivided into two types which are as follows:
- Byte Input Stream: Used to read byte data from different devices.
- Byte Output Stream: Used to write byte data to different devices.
2. Character Stream:
This stream is used to read or write character data. Character stream is again subdivided into 2 types which are as follows:
- Character Input Stream: Used to read character data from different devices.
- Character Output Stream: Used to write character data to different devices.
Owing to the fact that you know what a stream is, let’s polish up File Handling in Java by further understanding the various methods that are useful for performing operations on the files like creating, reading, and writing files.
Java File Class Methods
The following table depicts several File Class methods:
| Method Name | Description | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
| canRead() | It tests whether the file is readable or not. | Boolean |
| canWrite() | It tests whether the file is writable or not. | Boolean |
| createNewFile() | It creates an empty file. | Boolean |
| delete() | It deletes a file. | Boolean |
| exists() | It tests whether the file exists or not. | Boolean |
| length() | Returns the size of the file in bytes. | Long |
| getName() | Returns the name of the file. | String |
| list() | Returns an array of the files in the directory. | String[] |
| mkdir() | Creates a new directory. | Boolean |
| getAbsolutePath() | Returns the absolute pathname of the file. | String |
Let us now get acquainted with the various file operations in Java.
File operations in Java
The following are the several operations that can be performed on a file in Java :
Now let us study each of the above operations in detail.
1. Create a File
- In order to create a file in Java, you can use the createNewFile() method.
- If the file is successfully created, it will return a Boolean value true and false if the file already exists.
Following is a demonstration of how to create a file in Java :
File Handling in Java
File handling refers to working with the file in java. Reading files & writing into java files is known as file handling in java. The FIle is a container that can contain different types of information. The file can contain text, images, videos, tables, etc.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
In java, the File class enables us to work with different types of files. File class is a member of the java.io packages. Java provides various methods to read, write, update & delete files.
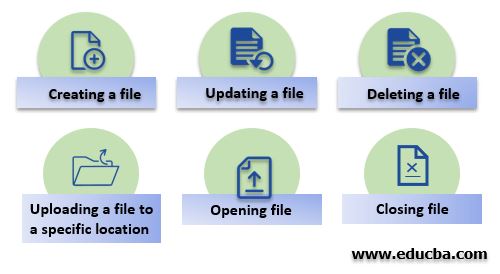
Types of Operation
Different types of operation which can be performed on a file is given below:
- Creating a file
- Updating a file
- Deleting a file
- Uploading a file to a specific location
- Opening file
- Closing file
Syntax:
To work with files in the program, you need to import the java.io package. Importing this package will provide you with a File class that you can initialize by referencing the file in the constructor of the File class.
//importing file class import java.io.File; //File name passed to the object File fileObj = new File("file.txt");How does file Handling work?
In Java, File handling takes place by streaming concepts. Input/Output operations on a file perform through streaming. Stream refers to a sequence of data.
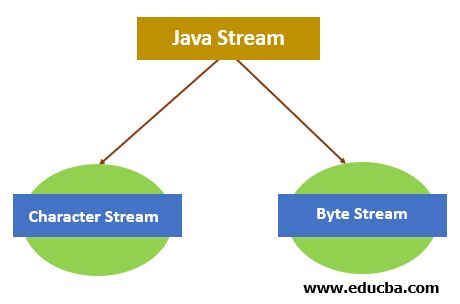
In java, Stream is of two types:
- Character Stream: A character stream refers to a stream that involves the characters. Data processing takes place with the Stream of characters in the files.
- Byte Stream: We call a stream that transfers data in bytes a byte stream. Data processing takes place with the Stream of bytes in the files.
File Handling Methods
Some of the methods are given below for performing different operations in java:
- createNewFile(): createNewFile method is used to create an empty file. It returns the response as a boolean.
- getName(): This method is used to get the file name. It returns the string, i.e., the file’s name in response.
- getAbsolutePath(): It returns the absolute path of the file. The return type of this method is a string.
- canRead(): This method checks whether the file is readable or not. It returns a boolean value.
- canWrite(): This method checks whether the file is writable or not. It returns a boolean value.
- delete(): This method is used in deleting a file. It returns a boolean value.
- exists(): Use this method to check if a file exists. It returns a boolean value.
- length(): This method returns the file size in bytes. The return type of this method is long.
- list(): This method returns an array of the files available in the directory. It returns an array of string values.
- mkdir(): To create a new directory, use this method. It returns a boolean value.
Examples of File Handling in Java
Below are examples of File Handling in Java:
Example #1
In this example, the program uses various methods to get specific details. In this application, different methods are used to get information related to files, such as:
- Retrieving the absolute path of the file.
- Checking whether the file is writable or not.
- Checking whether the file is readable or not.
- Retrieving file name.
- Retrieving file size.
- Obtaining a list of the files that are present in the specified directory, etc.
Importing io package different classes.
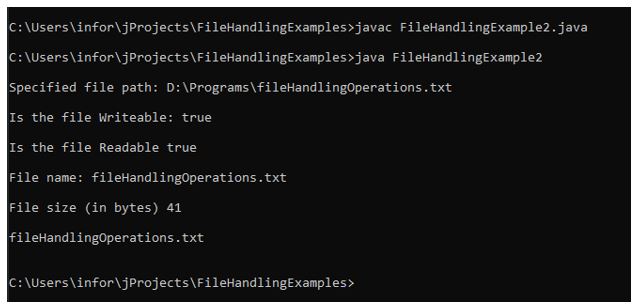
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class FileHandlingExample2 < public static void main(String[] args) < // Creating an object of a file File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt"); if (fileObj.exists()) < //retrieving the path of the specified file System.out.println("\nSpecified file path: " + fileObj.getAbsolutePath()); //checking whether the file is writable or not System.out.println("\nIs the file Writable: " + fileObj.canWrite()); //checking whether the file is Readable or not System.out.println("\nIs the file Readable " + fileObj.canRead()); //retrieving file name System.out.println("\nFile name: " + fileObj.getName()); //retrieving file size System.out.println("\nFile size (in bytes) " + fileObj.length()); File fileDirObj = new File("D:/Programs/"); String[] fileList = fileDirObj.list(); //displaying here the list of files available in the directory for (int i = 0; i < fileList.length; i++) < System.out.print("\n" + fileList[i]); >System.out.println("\n"); > else < System.out.println("Specified file does not exist."); >> >In the above-given example, we can see how different methods provide the information needed to perform the different checks related to files.
Example #2
This example shows how different methods are used in the program for different types of operations. exists() method used in the program to check if a file exists is not; after that, the if..else.. condition is placed.
In the If condition, it checks first whether the existing file is writable or not; if the existing file remains writable, then the code block under the if section uses the FileWriter class method to write content into the existing file.
Importing io package different classes.
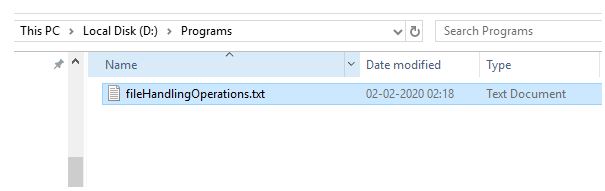
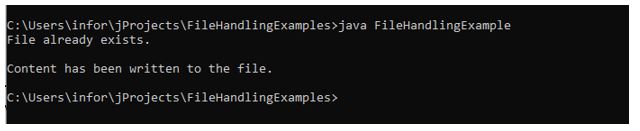
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class FileHandlingExample < public static void main(String[] args) < try < File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt"); if(fileObj.exists())< System.out.println("File already exists."); if(fileObj.canWrite())< //creating object of FileWriter class to write things on file FileWriter fwObj = new FileWriter("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt"); // Writes this content into the specified file fwObj.write("It is a basic example of writing in file!"); //closing the files once writing completed fwObj.close(); System.out.println("\nContent has been written to the file."); >else < System.out.println("\nFile is not in writable mode."); >; >else < if (fileObj.createNewFile()) < System.out.println("New File created: " + fileObj.getName()); >> > catch (IOException ioError) < System.out.println("An error occurred."); ioError.printStackTrace(); >> >In the above-given example, After compilation, running the program the first time will create a file with the specified name in the program.
Running the program a second time will write the content in the existing file.
Conclusion
The article above explains what a file is, how to perform operations on it, and how file handling works. It was also demonstrated in the above section about classes & methods that can be used to work with files in java.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to File Handling in Java. Here we discuss the basic concept, methods examples, and how file handling works in java. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
89+ Hours of HD Videos
13 Courses
3 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
97+ Hours of HD Videos
15 Courses
12 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
JAVA Course Bundle — 78 Courses in 1 | 15 Mock Tests
416+ Hours of HD Videos
78 Courses
15 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.8