Блочные элементы
Исторически HTML-элементы было принято делить на блочные и строчные. Блочные элементы занимают всю ширину своего родителя (контейнера), формально создавая «блок» (отсюда и название).
Браузеры обычно отображают блочные элементы с переводом строки до и после элемента. Блочные элементы можно представить в виде стопки коробок. Следующий пример демонстрирует, как это выглядит:
Блочные элементы
HTML
p> Этот абзац — блочный элемент; его цвет фона покрашен, чтобы показать родительский элемент абзаца. p>
CSS
p background-color: #8abb55; > Использование
Блочные против строчных
Существует несколько ключевых отличий между блочными и строчными элементами:
Как правило, блочные элементы могут содержать строчные элементы и другие блочные элементы. Неотъемлемой частью этого структурного различия является идея, что блочные элементы создают «более крупную» структуру, чем встроенные элементы.
Форматирование по умолчанию
По умолчанию блочные элементы начинаются с новой строки, а строчные могут начинаться в любом месте строки.
Разделение элементов на блочные и строчные использовалось в спецификации HTML до версии 4.01. В HTML5 это противопоставление заменено более сложным набором категорий контента. Категория «строчных» элементов примерно соответствует категории текстового контента, а для «блочных» элементов прямого соответствия нет, но «блочные» и «строчные» элементы вместе примерно соответствуют категории потокового контента в HTML5 (т.е., грубо говоря, «блочные» элементы — это потоковый контент минус текстовый контент). Кроме того, есть и другие категории, например, интерактивный контент.
Элементы
Ниже приведён полный список всех блочных элементов (хотя формально понятие «блочный» не применяется к новым элементам в HTML5).
Раскрывающийся блок с подробностями.
Block-level elements
In this article, we’ll examine HTML block-level elements and how they differ from inline-level elements.
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) elements historically were categorized as either «block-level» elements or «inline-level» elements. Since this is a presentational characteristic it is nowadays specified by CSS in the Flow Layout. A Block-level element occupies the entire horizontal space of its parent element (container), and vertical space equal to the height of its contents, thereby creating a «block».
Browsers typically display the block-level element with a newline both before and after the element. You can visualize them as a stack of boxes.
Note: A block-level element always starts on a new line and takes up the full width available (stretches out to the left and right as far as it can).
The following example demonstrates the block-level element’s influence:
Block-level elements
HTML
This paragraph is a block-level element; its background has been colored to display the paragraph's parent element.
CSS
Usage
Block-level vs. inline
There are a couple of key differences between block-level elements and inline elements:
Generally, block-level elements may contain inline elements and (sometimes) other block-level elements. Inherent in this structural distinction is the idea that block elements create «larger» structures than inline elements.
By default, block-level elements begin on new lines, but inline elements can start anywhere in a line.
The distinction of block-level vs. inline elements was used in HTML specifications up to 4.01. Later, this binary distinction is replaced with a more complex set of content categories. While the «inline» category roughly corresponds to the category of phrasing content, the «block-level» category doesn’t directly correspond to any HTML content category, but «block-level» and «inline» elements combined together correspond to the flow content in HTML. There are also additional categories, e.g. interactive content.
Elements
The following is a complete list of all HTML «block-level» elements (although «block-level» is not technically defined for elements that are new in HTML5).
HTML block level and inline elements
In general, HTML elements can be divided into two categories : block level and inline elements.
1. HTML block level elements can appear in the body of an HTML page.
2. It can contain another block level as well as inline elements.
3. By default, block-level elements begin on new lines.
4. block level elements create larger structures (than inline elements).
List of block level elements
- p
- h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6
- ol, ul
- pre
- address
- blockquote
- dl
- div
- fieldset
- form
- hr
- noscript
- table
Example of block level elements
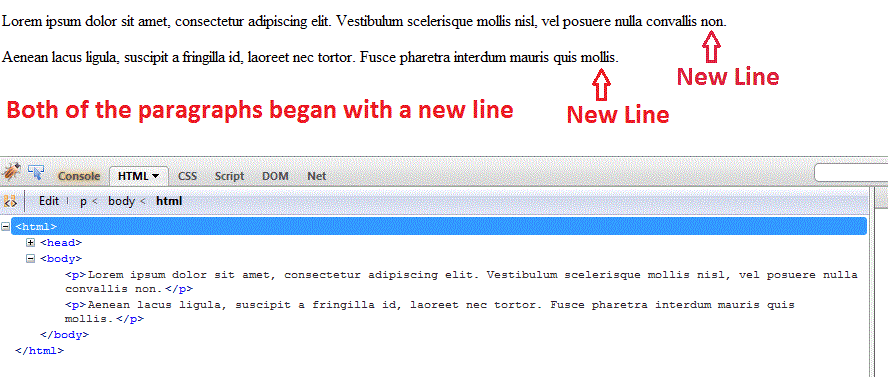
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vestibulum scelerisque mollis nisl, vel posuere nulla convallis non.
Aenean lacus ligula, suscipit a fringilla id, laoreet nec tortor. Fusce pharetra interdum mauris quis mollis.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vestibulum scelerisque mollis nisl, vel posuere nulla convallis non.
Aenean lacus ligula, suscipit a fringilla id, laoreet nec tortor. Fusce pharetra interdum mauris quis mollis.
Pictorial presentation
HTML inline elements
1. HTML inline level elements can appear in the body of an HTML page.
2. It can contain data and other inline elements.
3. By default, inline elements do not begin on new lines.
4. inline elements create shorter structures (than block level elements).
List of inline elements
- b, big, i, small, tt
- abbr, acronym, cite, code, dfn, em, kbd, strong, samp, var
- a, bdo, br, img, map, object, q, script, span, sub, sup
- button, input, label, select, textarea
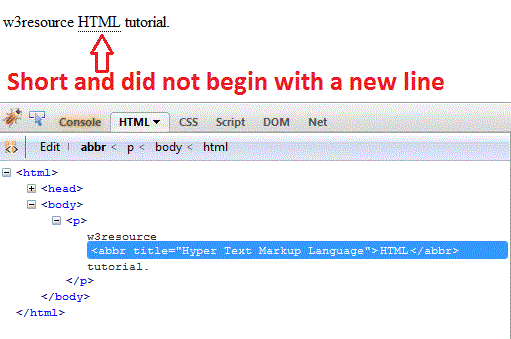
Example of inline elements
w3resource HTML tutorial.
Pictorial presentation
Test your Programming skills with w3resource’s quiz.
Follow us on Facebook and Twitter for latest update.
- Weekly Trends
- Java Basic Programming Exercises
- SQL Subqueries
- Adventureworks Database Exercises
- C# Sharp Basic Exercises
- SQL COUNT() with distinct
- JavaScript String Exercises
- JavaScript HTML Form Validation
- Java Collection Exercises
- SQL COUNT() function
- SQL Inner Join
- JavaScript functions Exercises
- Python Tutorial
- Python Array Exercises
- SQL Cross Join
- C# Sharp Array Exercises
We are closing our Disqus commenting system for some maintenanace issues. You may write to us at reach[at]yahoo[dot]com or visit us at Facebook