- How to Call a Function in Python (Example)
- How to define and call a function in Python
- Significance of Indentation (Space) in Python
- How Function Return Value?
- Arguments in Functions
- Here is the complete Python 3 code
- How to Define And Call Functions in Python
- How to Define a Function
- How to Call a Function
- Python Function Code Examples
- Conclusion
How to Call a Function in Python (Example)
A Function in Python is a piece of code which runs when it is referenced. It is used to utilize the code in more than one place in a program. It is also called method or procedure. Python provides many inbuilt functions like print(), input(), compile(), exec(), etc. but it also gives freedom to create your own functions.
How to define and call a function in Python
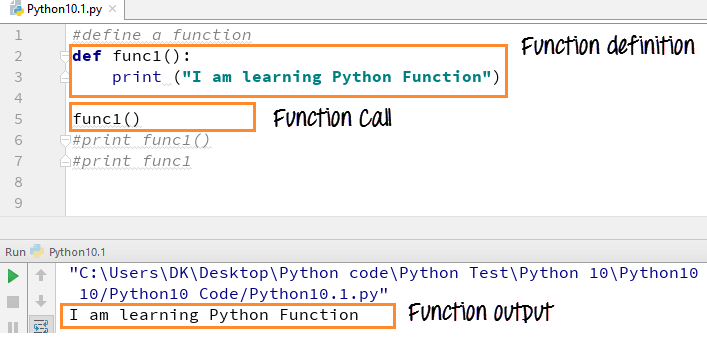
Function in Python is defined by the “def ” statement followed by the function name and parentheses ( () )
Let us define a function by using the command ” def func1():” and call the function. The output of the function will be “I am learning Python function”.
The function print func1() calls our def func1(): and print the command ” I am learning Python function None.“
There are set of rules in Python to define a function.
- Any args or input parameters should be placed within these parentheses
- The function first statement can be an optional statement- docstring or the documentation string of the function
- The code within every function starts with a colon (:) and should be indented (space)
- The statement return (expression) exits a function, optionally passing back a value to the caller. A return statement with no args is the same as return None.
Significance of Indentation (Space) in Python
Before we get familiarize with Python functions, it is important that we understand the indentation rule to declare Python functions and these rules are applicable to other elements of Python as well like declaring conditions, loops or variable.
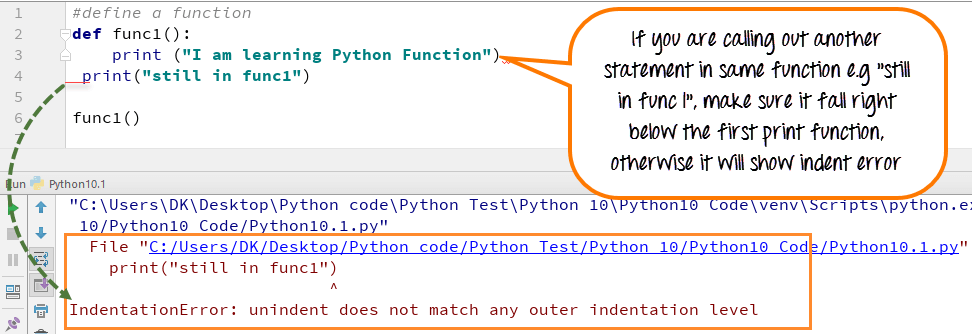
Python follows a particular style of indentation to define the code, since Python functions don’t have any explicit begin or end like curly braces to indicate the start and stop for the function, they have to rely on this indentation. Here we take a simple example with “print” command. When we write “print” function right below the def func 1 (): It will show an “indentation error: expected an indented block“.
Now, when you add the indent (space) in front of “print” function, it should print as expected.
At least, one indent is enough to make your code work successfully. But as a best practice it is advisable to leave about 3-4 indent to call your function.
It is also necessary that while declaring indentation, you have to maintain the same indent for the rest of your code. For example, in below screen shot when we call another statement “still in func1” and when it is not declared right below the first print statement it will show an indentation error “unindent does not match any other indentation level.”
Now, when we apply same indentation for both the statements and align them in the same line, it gives the expected output.
How Function Return Value?
Return command in Python specifies what value to give back to the caller of the function. Let’s understand this with the following example
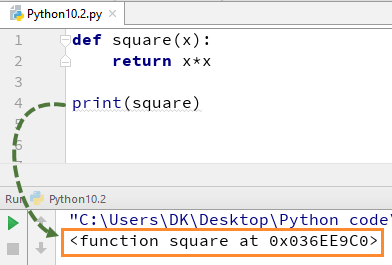
Step 1) The function does not return anything
Here – we see when function is not “return”. For example, we want the square of 4, and it should give answer “16” when the code is executed. Which it gives when we simply use “print x*x” code, but when you call function “print square” it gives “None” as an output. This is because when you call the function, recursion does not happen and fall off the end of the function. Python returns “None” for failing off the end of the function.
Step 2) Replace the print command with assignment command
To make this clearer we replace the print command with assignment command. Let’s check the output.
When you run the command “print square (4)” it actually returns the value of the object since we don’t have any specific function to run over here it returns “None”.
Step 3) Use ‘return’ function and execute the code
Now, here we will see how to retrieve the output using “return” command. When you use the “return” function and execute the code, it will give the output “16.”
Step 4) Run the command ‘print square’
Functions in Python are themselves an object, and an object has some value. We will here see how Python treats an object. When you run the command “print square” it returns the value of the object. Since we have not passed any argument, we don’t have any specific function to run over here it returns a default value (0x021B2D30) which is the location of the object. In practical Python program, you probably won’t ever need to do this.
Arguments in Functions
The argument is a value that is passed to the function when it’s called.
In other words on the calling side, it is an argument and on the function side it is a parameter.
Let see how Python Args works –
Step 1) Arguments are declared in the function definition. While calling the function, you can pass the values for that args as shown below
Step 2) To declare a default value of an argument, assign it a value at function definition.
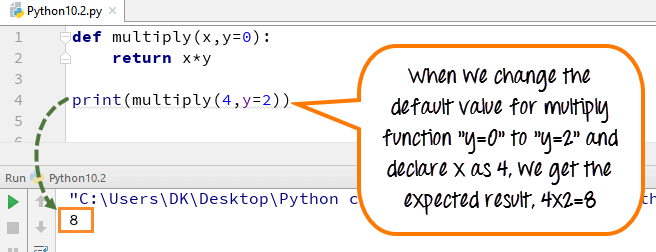
Example: x has no default values. Default values of y=0. When we supply only one argument while calling multiply function, Python assigns the supplied value to x while keeping the value of y=0. Hence the multiply of x*y=0
Step 3) This time we will change the value to y=2 instead of the default value y=0, and it will return the output as (4×2)=8.
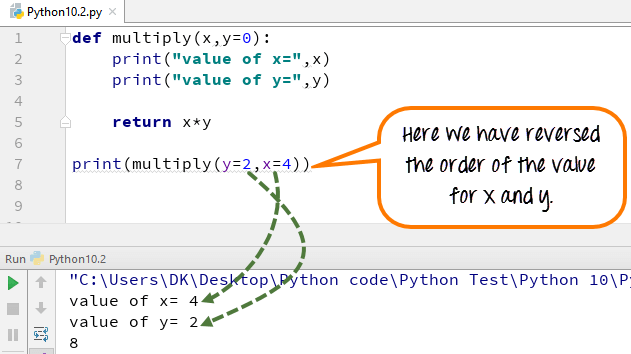
Step 4) You can also change the order in which the arguments can be passed in Python. Here we have reversed the order of the value x and y to x=4 and y=2.
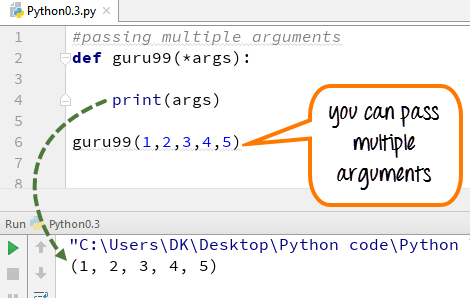
Step 5) Multiple Arguments can also be passed as an array. Here in the example we call the multiple args (1,2,3,4,5) by calling the (*args) function.
Example: We declared multiple args as number (1,2,3,4,5) when we call the (*args) function; it prints out the output as (1,2,3,4,5)
- In Python 2.7. function overloading is not supported in Python. Function Overloading is the ability to create multiple methods of the same name with a different implementation. Function Overloading is fully supported in Python 3
- There is quite a confusion between methods and functions. Methods in Python are associated with object instances while function are not. When Python calls a method, it binds the first parameter of that call to the appropriate object reference. In simple words, a standalone function in Python is a “function”, whereas a function that is an attribute of a class or an instance is a “method”.
Here is the complete Python 3 code
#define a function def func1(): print («I am learning Python function») print («still in func1») func1() def square(x): return x*x print(square(4)) def multiply(x,y=0): print(«value of x=»,x) print(«value of y codepython»>#define a function def func1(): print » I am learning Python function» print » still in func1″ func1() def square(x): return x*x print square(4) def multiply(x,y=0): print»value of x=»,x print»value of y rocketlazyloadscript» src=»https://www.guru99.com/wp-includes/js/jquery/jquery.min.js»>
How to Define And Call Functions in Python
Oluseye Jeremiah
Python is a powerful and versatile programming language that offers a wide range of functionalities for developers.
One of the most essential features of Python is the ability to define and call functions.
A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. In Python, defining and calling functions is easy and can greatly improve the readability and reusability of your code.
How to Define a Function
Defining a function in Python involves two main steps: defining the function and specifying the arguments it takes.
To define a function, you use the def keyword followed by the name of the function and parentheses (). If the function takes any arguments, they are included within the parentheses. The code block for the function is then indented after the colon.
def greet(name): print("Hello, " + name + "! How are you?") In this example, we define a function called greet that takes one argument called name . The function then prints out a greeting message to the console that includes the name argument.
How to Call a Function
Once you have defined a function, you can call it in your code as many times as you need.
To call a function in Python, you simply type the name of the function followed by parentheses (). If the function takes any arguments, they are included within the parentheses.
In this example, we call the greet function with the argument «John». The output to the console would be:
Python Function Code Examples
Here’s a complete code example that defines and calls the greet function:
def greet(name): print("Hello, " + name + "! How are you?") greet("John") When you run this code, it will output the following to the console:
Let’s take a more advanced example of defining and calling functions in Python.
Let’s say you want to write a function that takes in a list of integers and returns a new list with all the even numbers in the original list. Here’s how you could define and call this function:
def get_even_numbers(numbers): even_numbers = [] for number in numbers: if number % 2 == 0: even_numbers.append(number) return even_numbers numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] even_numbers = get_even_numbers(numbers) print(even_numbers) In this example, we define a function called get_even_numbers that takes one argument called numbers. The function then creates an empty list called even_numbers and loops through each number in the numbers list.
If the number is even, it is added to the even_numbers list using the append method. Finally, the function returns the even_numbers list.
To call this function, we first create a list of numbers called numbers with the values [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]. We then call the get_even_numbers function with the numbers list as an argument and assign the returned value to a new list called even_numbers.
Finally, we print out the even_numbers list to the console.
When you run this code, it will output the following to the console:
This is the list of even numbers in the original numbers list.
This example demonstrates how to define a more complex function that performs a specific task, and how to call that function with the appropriate arguments.
By breaking down complex tasks into smaller, reusable functions, you can make your code more readable, maintainable, and efficient.
Conclusion
Defining and calling functions in Python is a straightforward process that can greatly improve the functionality and readability of your code.
With Python’s simple syntax and powerful capabilities, you can define and call functions with any number of arguments and perform any number of tasks within the function code block.
So go ahead and start defining and calling functions in your Python code to take your programming skills to the next level.