- How to import CSV file into an SQLite Table using Python?
- Related Posts:
- Creating a sqlite database from CSVs with Python
- Creating a sqlite database
- Creating sqlite table
- Load CSV file into sqlite table
- Fetch values from sqlite table
- Load another CSV into the databases
- Fetch results of database join
- Next steps
- Registration
- 1 Comment
- Primary Sidebar
- Recent Posts
- Recent Comments
- Archives
- Categories
- Meta
- Import a CSV File to SQL Server using Python
- Steps to Import a CSV file to SQL Server using Python
- Step 1: Prepare the CSV File
- Step 2: Import the CSV File into a DataFrame
- Step 3: Connect Python to SQL Server
- Step 4: Create a Table in SQL Server using Python
- Step 5: Insert the DataFrame Data into the Table
- Step 6: Perform a Test
How to import CSV file into an SQLite Table using Python?
In this post, we will see how to import CSV file data into an SQLite database table using Python.
Now, For solving this requirement we will be using two modules: sqlite3 and pandas. So let’s discuss these first.
sqlite3 module is used to access SQLite databases in Python. SQLite is a self-contained, high-reliability, embedded, full-featured, public-domain, SQL database engine. It is the most used database engine on the world wide web.
Pandas is an open-source library that is built on top of the NumPy library. It is a Python package that offers various data structures and operations for manipulating numerical data and time series. It is mainly popular for importing and analyzing data much easier. Pandas is fast and it has high performance & productivity for users.
Now, Let’s see the approach to import CSV file data into an SQLite database table using Python.
Approach:
Syntax: import moduleName
- Make a connection object with the existing database or create a new database and connect it using connect() class of sqlite3 module.
Syntax: sqlite3.connect(‘databaseName.db’)
Syntax: connection_object.cursor()
- Create a new table by executing create SQL query using execute() method of cursor object.
Syntax: cursor_object.execute("Sql Query") Syntax: pandas.read_csv(‘file_name.csv’)
The function to_sql() creates a new table from records of the dataframe. Pass the table name and connection object inside this function. The column names of the table are the same as the header of the CSV file. By default, the dataframe index is written as a column. Simply toggle the index parameter to False in order to remove this column. Additionally, the if_exists parameter specifies the behavior in case the table name is already being used. It can either raise an error (fail), append new values, or replace the existing table.
Syntax: DataFrame.to_sql(table_name, connection_object, if_exists, index)
Syntax: connection_object.close()
Now, let’s look into Python code:
# Import sqlite3 module into # this program as sq import sqlite3 as sq # Import pandas module into # this program as pd import pandas as pd # Create a connection object, # Make a new db if not exist already # and connect it, if exist then connect. connection = sq.connect('information.db') # Create a cursor object curs = connection.cursor() # Run create table sql query curs.execute("create table if not exists studentInfo" + " (name text, gender text, age integer,course text, branch text)") # Load CSV data into Pandas DataFrame student = pd.read_csv('student.csv') # Write the data to a sqlite db table student.to_sql('studentInfo', connection, if_exists='replace', index=False) # Run select sql query curs.execute('select * from studentInfo') # Fetch all records # as list of tuples records = curs.fetchall() # Display result for row in records: # show row print(row) # Close connection to SQLite database connection.close() Output:
You can access the CSV file Here.
Related Posts:
Creating a sqlite database from CSVs with Python
This blog post demonstrates how to build a sqlite database from CSV files.
Python is perfect language for this task because it has great libraries for sqlite and CSV DataFrames.
Creating a sqlite database
sqlite is a lightweight database that can be started as an empty text file. You can create the file with touch my_data.db or with this equivalent Python code:
from pathlib import Path Path('my_data.db').touch() A zero byte text file is a great starting point for a lightweight database!
Creating sqlite table
Create a database connection and cursor to execute queries.
import sqlite3 conn = sqlite3.connect('my_data.db') c = conn.cursor() Execute a query that’ll create a users table with user_id and username columns.
c.execute('''CREATE TABLE users (user_id int, username text)''') Load CSV file into sqlite table
Suppose you have the following users.csv file:
user_id,username 1,pokerkid 2,crazyken
Pandas makes it easy to load this CSV data into a sqlite table:
import pandas as pd # load the data into a Pandas DataFrame users = pd.read_csv('users.csv') # write the data to a sqlite table users.to_sql('users', conn, if_exists='append', index = False) The to_sql method makes it easy to write DataFrames to databases.
Fetch values from sqlite table
Fetch all the rows from the users table:
c.execute('''SELECT * FROM users''').fetchall() # [(1, 'pokerkid'), (2, 'crazyken')] The fetchall() method returns an array of tuples.
c.execute() returns a sqlite3.Cursor object. Cursors can be thought of as iterators in the database world.
Load another CSV into the databases
Suppose you have the following orders.csv file:
order_id,user_id,item_name 1,1,speaker 2,1,phone 3,2,spoon 4,2,fork 5,2,speaker
Create a table and then load the orders data into the database.
c.execute('''CREATE TABLE orders (order_id int, user_id int, item_name text)''') orders = pd.read_csv('orders.csv') # load to DataFrame orders.to_sql('orders', conn, if_exists='append', index = False) # write to sqlite table Fetch results of database join
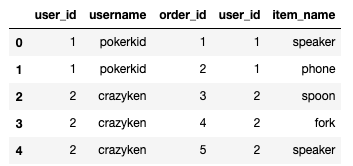
Join the users and orders tables on the user_id value and print the results:
c.execute('''SELECT * FROM users u LEFT JOIN orders o ON u.user_id = o.user_id''') c.fetchall() Here’s the array that’s returned:
[(1, 'pokerkid', 1, 1, 'speaker'), (1, 'pokerkid', 2, 1, 'phone'), (2, 'crazyken', 3, 2, 'spoon'), (2, 'crazyken', 4, 2, 'fork'), (2, 'crazyken', 5, 2, 'speaker')]
You can also read the SQL query directly into a Pandas DataFrame.
pd.read_sql('''SELECT * FROM users u LEFT JOIN orders o ON u.user_id = o.user_id''', conn) Next steps
Python’s build in sqlite library coupled with Pandas DataFrames makes it easy to load CSV data into sqlite databases.
sqlite databases are great for local experimentation and are used extensively on mobile phones. It’s a great database when you’d like relational database query functionality without the overhead of Postgres.
Python’s great support for sqlite will make you love it in no time.
Registration
1 Comment
what i need to do if i have more than one file csv and that i want to upload to create sqlite dat frame
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.
Primary Sidebar
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
- Chris Winne on Chaining Custom PySpark DataFrame Transformations
- KAYSWELL on Serializing and Deserializing Scala Case Classes with JSON
- mrpowers on Exploring DataFrames with summary and describe
- carlo sancassani on Calculating Week Start and Week End Dates with Spark
- Andrew on Exploring DataFrames with summary and describe
Archives
Categories
Meta
Copyright © 2023 MungingData. Powered by WordPress and Stargazer.
Import a CSV File to SQL Server using Python
There is more than one way to import a CSV file to SQL Server using Python. In this guide, you’ll see a simple technique to import your data using the following 2 Python libraries:
- Pandas – used to import the CSV file into Python and create a DataFrame
- Pyodbc – used to connect Python to SQL Server
Steps to Import a CSV file to SQL Server using Python
Step 1: Prepare the CSV File
To begin, prepare the CSV file that you’d like to import to SQL Server.
For example, let’s assume that a CSV file was prepared, where:
- The CSV file name is ‘products’
- The CSV file is stored under the following path: C:\Users\Ron\Desktop\Test\products.csv
In addition, the CSV file contains the following data:
| product_id | product_name | price |
| 1 | Laptop | 1200 |
| 2 | Printer | 200 |
| 3 | Tablet | 350 |
| 4 | Keyboard | 80 |
| 5 | Monitor | 400 |
Step 2: Import the CSV File into a DataFrame
You may use the Pandas library to import the CSV file into a DataFrame.
Here is the code to import the CSV file for our example (note that you’ll need to change the path to reflect the location where the CSV file is stored on your computer):
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv (r'C:\Users\Ron\Desktop\Test\products.csv') df = pd.DataFrame(data) print(df)
This is how the DataFrame would look like in Python:
product_id product_name price 0 1 Laptop 1200 1 2 Printer 200 2 3 Tablet 350 3 4 Keyboard 80 4 5 Monitor 400 Step 3: Connect Python to SQL Server
To connect Python to SQL server, you’ll need the:
- Server Name. For demonstration purposes, let’s assume that the server name is: RON\SQLEXPRESS
- Database Name. The database name for our example would be: test_database
Here is the code to connect Python to SQL for our example:
import pyodbc conn = pyodbc.connect('Driver=;' 'Server=RON\SQLEXPRESS;' 'Database=test_database;' 'Trusted_Connection=yes;') cursor = conn.cursor() You may wish to check the following guide that explains the full steps to connect Python to SQL Server using pyodbc.
Step 4: Create a Table in SQL Server using Python
Next, add the syntax to create the table in SQL Server. This table will be used to store the imported data from the CSV file.
For our example, you can add the following syntax to create the ‘products‘ table:
cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE products ( product_id int primary key, product_name nvarchar(50), price int ) ''') Note that whenever you run the code to create a table. You should only use that piece of the code once. Otherwise, you’ll get the error below:
ProgrammingError: (’42S01′, “[42S01] [Microsoft][ODBC SQL Server Driver][SQL Server]There is already an object named ‘products’ in the database. (2714) (SQLExecDirectW)”)
Step 5: Insert the DataFrame Data into the Table
Here is the syntax to insert the DataFrame data (from step-2) into the products table:
for row in df.itertuples(): cursor.execute(''' INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name, price) VALUES (. ) ''', row.product_id, row.product_name, row.price ) conn.commit() And here is the entire code to import the CSV file into SQL Server using Python:
import pandas as pd import pyodbc # Import CSV data = pd.read_csv (r'C:\Users\Ron\Desktop\Test\products.csv') df = pd.DataFrame(data) # Connect to SQL Server conn = pyodbc.connect('Driver=;' 'Server=RON\SQLEXPRESS;' 'Database=test_database;' 'Trusted_Connection=yes;') cursor = conn.cursor() # Create Table cursor.execute(''' CREATE TABLE products ( product_id int primary key, product_name nvarchar(50), price int ) ''') # Insert DataFrame to Table for row in df.itertuples(): cursor.execute(''' INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name, price) VALUES (. ) ''', row.product_id, row.product_name, row.price ) conn.commit() Run the code in Python (after making the adjustment to the path where your CSV file is stored, as well as making the change to your database connection info).
Step 6: Perform a Test
Let’s run a simple query to check that the values from the CSV file got imported into SQL Server:
| product_id | product_name | price |
| 1 | Laptop | 1200 |
| 2 | Printer | 200 |
| 3 | Tablet | 350 |
| 4 | Keyboard | 80 |
| 5 | Monitor | 400 |