- Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally + Vertically With CSS
- How to Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally and Vertically With CSS?
- Method 1: How to Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally and Vertically Using “transform: scale()” Property?
- Method 2: How to Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally and Vertically Using “transform: rotate()” Property?
- How to Flip/Mirror an Image Vertically or Horizontally on Hover?
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Nadia Bano
- How TO — Flip an Image
- How To Flip an Image
- Example
- Add Transition
- Example
- 3D Flip Image with Text
- Paris
- Example
- Paris
- Example
- Flipping Images Horizontally Or Vertically With CSS And JavaScript
- Flipping an Image Element
- Flipping a Background Image
- Flipping an Image with JavaScript
- Conclusion
Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally + Vertically With CSS
Images are an essential and entertaining application component. They contribute to the application’s design and give it a beautiful layout. Many of the properties offered by CSS are beneficial in various ways. More specifically, it provides features that allow image adjustment in any direction, such as flipping vertically or horizontally, rotating, and more.
This write-up will guide you on how to flip or mirror an image horizontally and vertically with CSS.
How to Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally and Vertically With CSS?
There are various methods that can be used to flip or rotate the images in CSS. We will discuss the following:
Method 1: How to Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally and Vertically Using “transform: scale()” Property?
The “transform: scale()” property resizes the image in the 2D plane. The scale() specifies two coordinate values for the x-axis and y-axis. The amount of scaling done in each direction is determined by its coordinates. The “transform: scaleX()” property scales the image horizontally.
Add two images in the HTML file. The first one will be kept as original throughout the example. While the other one will be applied with the CSS properties:
- The “ ” tag is utilized to include an image.
- The “src” attribute specifies the image’s URL.
- The “alt” is utilized to specify the text if the image does not load to the web page.
- The “width” attribute sets the image’s breadth.
- The “class” is set with a name to access the image in CSS.
Here is the HTML code of the scenario as mentioned earlier:
Initially, the web page will look like this:
Example 1: Flipping the Image Horizontally Using the “transform: scaleX()” Property
In CSS, add the “transform: scaleX()” property to scale the image horizontally:
Example 2: Flipping the Image Vertically Using the “transform: scaleY()” Property
To scale the image vertically in CSS, use the “transform: scaleY()” property:
Method 2: How to Flip/Mirror an Image Horizontally and Vertically Using “transform: rotate()” Property?
The CSS “transform: rotate()” rotates the image around the fixed point in a 2D plane. The “rotateX()” function rotates the image on the x-axis, and the “rotateY()” is utilized to rotate on the y-axis.
Example 1: Flipping the Image Horizontally Using the “transform: rotateY()” Property
In CSS, add the “transform” property with the value “rotateY()” in the “flip” class to flip the image horizontally at “180” degrees:
Example 2: Flipping the Image Vertically Using the “transform: rotateX()” Property
Add the CSS “transform” property with the value “rotateX()” to flip the image vertically:
How to Flip/Mirror an Image Vertically or Horizontally on Hover?
To learn how to flip an image vertically or horizontally on hover, try out the following steps.
Step 1: Create an HTML File
First, follow the provided steps to create an HTML file:
- Add a “ ” element and assign it a class “flip-box”.
- Inside this card, add another “” with the class “flip-card”.
- Then, add an “ ” tag with the “src”, “alt”, and “style” attributes.
Step 2: Style “flip-box” Class
The “.flip-box” used to access the container with the class “flip-box”:
The properties that are mentioned in the above code snippet are described below:
- “position” property with the value “relative” sets the element’s position according to its current location.
- The “width” and “height” properties are utilized to set the element’s area.
- “margin” property adds spaces around the element.
Step 3: Style “flip-card” Class
Now, style the “flip-card” class:
The description of the above-provided properties is mentioned below:
- “position” with the “absolute” value sets the element’s location relative to the nearly positioned element.
- “transition” property adjusts the slow movement of the elements within a specified duration.
Step 4: Style “img” Element
The “ ” element is styled with the CSS “border-radius” property:
Here, the “border-radius” property sets the image corners as round.
Step 5: Flip an Image Vertically on Hover
To flip the image on hover, the CSS “:hover” pseudo-class has been utilized:
Step 6: Flip an Image Horizontally on Hover
The “transform: rotateY()” property can be utilized to flip the image horizontally:
We have compiled the approaches to flip/mirror an image horizontally and vertically with CSS.
Conclusion
To flip an image in HTML, the CSS “transform” property with the values “scale()” and “rotate()” are utilized. The “scaleX()” and “rotateY()” are adjusted to flip the image horizontally. The “scaleY()” and “rotateX()” are set to flip the image vertically. To add a hover effect, the CSS “:hover” pseudo-class is applied. This post has explained multiple procedures on how to flip an image horizontally and vertically in CSS.
About the author
Nadia Bano
I am an enthusiastic and forward-looking software engineer with an aim to explore the global software industry. I love to write articles on advanced-level designing, coding, and testing.
How TO — Flip an Image
Learn how to flip an image (add a mirror effect) with CSS.
Move your mouse over the image:
How To Flip an Image
Example
Add Transition
You can also add a transition effect to «fade» the flip:
Example
Note: This example does not work on tablets or mobile phones.
Tip: Go to our CSS 3D Transforms Tutorial, to learn more about 3D transformations.
3D Flip Image with Text
Learn how to do an animated 3D flip of an image with text:
Paris
Step 1) Add HTML:
Example

Paris
What an amazing city
Step 2) Add CSS:
Example
/* The flip box container — set the width and height to whatever you want. We have added the border property to demonstrate that the flip itself goes out of the box on hover (remove perspective if you don’t want the 3D effect */
.flip-box background-color: transparent;
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #f1f1f1;
perspective: 1000px; /* Remove this if you don’t want the 3D effect */
>
/* This container is needed to position the front and back side */
.flip-box-inner position: relative;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
text-align: center;
transition: transform 0.8s;
transform-style: preserve-3d;
>
/* Do an horizontal flip when you move the mouse over the flip box container */
.flip-box:hover .flip-box-inner transform: rotateY(180deg);
>
/* Position the front and back side */
.flip-box-front, .flip-box-back position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
-webkit-backface-visibility: hidden; /* Safari */
backface-visibility: hidden;
>
/* Style the front side (fallback if image is missing) */
.flip-box-front background-color: #bbb;
color: black;
>
/* Style the back side */
.flip-box-back background-color: dodgerblue;
color: white;
transform: rotateY(180deg);
>
Flipping Images Horizontally Or Vertically With CSS And JavaScript
In this 3 minute article we’ll look at flipping images horizontally and vertically using CSS and JavaScript. We’ll explore how to flip an img element, a background-image , or flip the actual ImageData using a canvas element.
Flipping an Image Element
We can flip the img element using the CSS transform property. We can do so using the scaleX and scaleY transforms.
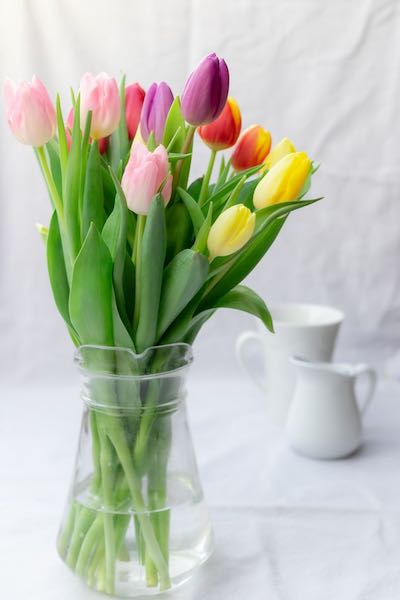
img src="/media/tulips.jpg" alt="" />img /* flip horizontally */ transform: scaleX(-1); > img /* flip vertically */ transform: scaleY(-1); > img /* flip both */ transform: scale(-1, -1); >original
scaleX(-1)
scaleY(-1)
scale(-1, -1)
Alternatively you can use rotateX and rotateY
img /* flip horizontally */ transform: rotateY(180deg); > img /* flip vertically */ transform: rotateX(180deg); > img /* flip both */ transform: rotateX(180deg) rotateY(180deg); >original
rotateY(180deg)
rotateX(180deg)
rotateX(180deg)
rotateY(180deg)
The rotation transform is also a nice choice for when you want to animate the flip.
scaleX
rotateY
Note that I’ve added a slight perspective to the transform chain. Without the perspective transform the rotateY animation would be just as flat as the scaleX animation. I’ve added it to the scaleX animation as well to show that it doesn’t make a difference.
@keyframes flip-with-scale 0% transform: perspective(400px) scaleX(1); > 100% transform: perspective(400px) scaleX(-1); > > @keyframes flip-with-rotate 0% transform: perspective(400px) rotateY(0); > 100% transform: perspective(400px) rotateY(180deg); > >Flipping a Background Image
The only way (at this point in time) (and as far as I can tell) to flip a background-image is to flip the element containing the background image. But that would flip its contents as well.
p class="tulips"> Tulips form a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes. p>.tulips background-image: url(/media/tulips.jpg); background-repeat: no-repeat; background-size: contain; padding-left: 5em; > .tulips-flipped transform: scaleX(-1); >Tulips form a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes.
Tulips form a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes.
To work around this we can either move the background to a separate element or create a pseudo-element.
Let’s go with the pseudo-element.
.tulips display: flex; width: 15em; > /* create our pseudo element */ .tulips-flipped::before content: ''; background-image: url(/media/tulips.jpg); background-repeat: no-repeat; background-size: cover; min-width: 5em; > /* flip our pseudo element */ .tulips-flipped::before transform: scaleX(-1); >Tulips form a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes.
Tulips form a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes.
Flipping an Image with JavaScript
The CSS flipping techniques only alter the presentation of an image, not the actual pixel data. We can flip the pixel data using the canvas element. This might be useful if for example we want to flip an image before it’s uploaded to a server.
We’ll use the image data in the image element below the code snippet, it’s simply an img tag with a class name set to image-tulips .
img src="/media/tulips.jpg" class="image-tulips" alt="" />Lets get a reference to the image. That allows us to load it to a canvas element for manipulation.
const inputImage = document.querySelector('.image-tulips'); // need to check if the image has already loaded if (inputImage.complete) flipImage(); > // if not, we wait for the onload callback to fire else inputImage.onload = flipImage; > // this function will flip the imagedata function flipImage() // create a canvas that will present the output image const outputImage = document.createElement('canvas'); // set it to the same size as the image outputImage.width = inputImage.naturalWidth; outputImage.height = inputImage.naturalHeight; // get the drawing context, needed to draw the new image const ctx = outputImage.getContext('2d'); // scale the drawing context negatively to the left (our image is 400 pixels wide) // resulting change to context: 0 to 400 -> -400 to 0 ctx.scale(-1, 1); // draw our image at position [-width, 0] on the canvas, we need // a negative offset because of the negative scale transform ctx.drawImage(inputImage, -outputImage.width, 0); // insert the output image after the input image inputImage.parentNode.insertBefore( outputImage, inputImage.nextElementSibling ); >The above code just ran, and you can view the result below. The first image is the inputImage and the second image is the outputImage canvas element.
Conclusion
We learned three methods to flip images for various purposes. We can flip images using the CSS transform property. The scaleX and scaleY transforms work but the rotateX and rotateY transforms allow for nicer animation (if needed). We quickly explored flipping background images using pseudo elements and ended the article with manipulating the actual image data using JavaScript and a canvas element.
I share web dev tips on Twitter, if you found this interesting and want to learn more, follow me there
At PQINA I design and build highly polished web components.
Make sure to check out FilePond a free file upload component, and Pintura an image editor that works on every device.