- Адаптивный и мобильный дизайн с CSS3 Media Queries
- Для начала посмотрим это в действии.
- Другие примеры
- Обзор
- HTML
- HTML5.js
- CSS
- Сбрасываем HTML5 элементы в block
- Описываем основную структуру в CSS
- Шаг 1
- CSS3 Media Queries
- Подключаем Media Queries Javascript
- Подключаем CSS media queries
- Размер экрана меньше 980px (резиновый макет)
- Размер экрана меньше 650px (одноколоночный макет)
- Размер экрана меньше 480px
- Эластичные изображения
- Эластичные встраиваемые видео
- Initial Scale Meta Tag (iPhone)
- Финальное Демо
- HTML Responsive Web Design
- What is Responsive Web Design?
- Setting The Viewport
- Example
- Responsive Images
- Using the width Property
- Example
- Using the max-width Property
- Example
- Example
- Responsive Text Size
- Hello World
- Example
- Hello World Viewport is the browser window size. 1vw = 1% of viewport width. If the viewport is 50cm wide, 1vw is 0.5cm. Media Queries In addition to resize text and images, it is also common to use media queries in responsive web pages. With media queries you can define completely different styles for different browser sizes. Example: resize the browser window to see that the three div elements below will display horizontally on large screens and stack vertically on small screens: Example .main float: left; width: 60%; /* The width is 60%, by default */ > /* Use a media query to add a breakpoint at 800px: */ @media screen and (max-width: 800px) .left, .main, .right width: 100%; /* The width is 100%, when the viewport is 800px or smaller */ > > Tip: To learn more about Media Queries and Responsive Web Design, read our RWD Tutorial. Responsive Web Page — Full Example A responsive web page should look good on large desktop screens and on small mobile phones. Ever heard about W3Schools Spaces? Here you can create your website from scratch or use a template, and host it for free. Responsive Web Design — Frameworks All popular CSS Frameworks offer responsive design. They are free, and easy to use. W3.CSS W3.CSS is a modern CSS framework with support for desktop, tablet, and mobile design by default. W3.CSS is smaller and faster than similar CSS frameworks. W3.CSS is designed to be independent of jQuery or any other JavaScript library. W3.CSS Demo Resize the page to see the responsiveness! London London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants. Paris Paris is the capital of France. The Paris area is one of the largest population centers in Europe, with more than 12 million inhabitants. Tokyo Tokyo is the capital of Japan. It is the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, and the most populous metropolitan area in the world. Example W3Schools Demo Resize this responsive page!
Адаптивный и мобильный дизайн с CSS3 Media Queries
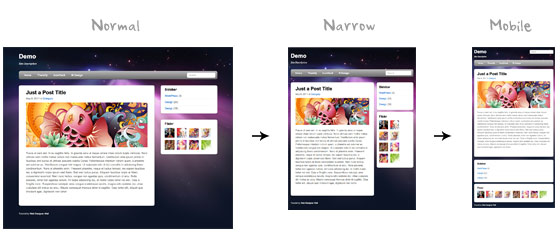
Разрешение экрана в наши дни колеблется от 320px (iPhone) до 2560px (большие мониторы) или даже выше. Пользователи больше не просматривают сайты только на настольных компьютерах. Теперь пользователи используют мобильные телефоны, небольшие ноутбуки, планшетные устройства, такие как iPad или Playbook для доступа в интернет. Поэтому, традиционный дизайн с фиксированной шириной больше не работает. Дизайн должен быть адаптивным. Структура должна автоматически изменяться с учетом всех разрешений дисплеев. Эта статья покажет вам как создавать кросс-браузерный адаптивный дизайн при помощи HTML5 и CSS3 media queries.
Для начала посмотрим это в действии.
Пред началом посмотрите на финальное демо, что бы увидеть, как хорошо это выглядит. Изменяйте размер браузера, что бы увидеть как структура автоматически изменяется основываясь на ширине окна.
Другие примеры
Если вы хотите увидеть больше примеров, посмотрите следующие темы для WordPress, которые я сделал используя media queries: iTheme2, Funki, Minblr и Wumblr.
Обзор
Контейнер страницы имеет ширину 980px для любого разрешения, больше 1024px. Для проверки ширины используются media queries, если ширина меньше чем 980px, в этом случае макет становится резиновым, вместо фиксированной ширины. Если ширина меньше 650px, то контейнеры с контентом и боковой панелью расширяются на полный экран и становятся в одну колонку.
HTML
Не будем останавливаться на подробном описании HTML. Ниже описана основная структура макета. У меня есть «pagewrap», который включает в себя «header», «content», «sidebar» и «footer».
HTML5.js
Обратите внимание, что в демо используется HTML5. Internet Explorer ниже 9-й версии не поддерживает новые элементы содержащиеся в HTML5, такие как , , , и прочие. Поэтому подключаем Javascript файл html5.js в HTML документ, который позволит IE понимать новые элементы.
CSS
Сбрасываем HTML5 элементы в block
article , aside , details , figcaption , figure , footer , header , hgroup , menu , nav , section <
display : block ;
>
Описываем основную структуру в CSS
Я снова не буду вдаваться в подробности. Основной контейнер «pagewrap» имеет ширину 980px. «Header» имеет фиксированную высоту 160px. Контейнер «content» шириной 600px и прижат влево. «Sidebar» шириной 280px и прижат вправо.
#pagewrap <
width : 980px ;
margin : 0 auto ;
>
#header <
height : 160px ;
>
#content <
width : 600px ;
float : left ;
>
#sidebar <
width : 280px ;
float : right ;
>
#footer <
clear : both ;
>
Шаг 1
На первом шаге в демо не реализованы media queries, поэтому при изменении размера окна браузера, макет будет оставаться фиксированной ширины.
CSS3 Media Queries
Теперь начинается самое интересное – media queries.
Подключаем Media Queries Javascript
Internet Explorer 8 и более ранних версий не поддерживает CSS3 media queries. Вы можете включить ее, добавив Javascript файл css3-mediaqueries.js.
Подключаем CSS media queries
Создаем новый CSS файл для media queries. Посмотрите мою прошлую статью, что бы увидеть как работают media queries.
Размер экрана меньше 980px (резиновый макет)
@media screen and (max-width: 980px) <
#pagewrap <
width : 95 % ;
>
#content <
width : 60 % ;
padding : 3 % 4 % ;
>
#sidebar <
width : 30 % ;
>
#sidebar .widget <
padding : 8 % 7 % ;
margin-bottom : 10px ;
>
>
Размер экрана меньше 650px (одноколоночный макет)
- header = сбрасываем высоту в auto;
- searchform = позиционируем — 5px сверху;
- main-nav = сбрасываем позиционирование в static;
- site-logo = сбрасываем позиционирование в static;
- site-description = сбрасываем позиционирование в static;
- content = устанавливаем ширину auto (это растянет контейнер на всю ширину)
- sidebar = устанавливаем ширину 100% и убираем float.
@media screen and (max-width: 650px) <
#header <
height : auto ;
>
#searchform <
position : absolute ;
top : 5px ;
right : 0 ;
>
#main-nav <
position : static ;
>
#site-logo <
margin : 15px 100px 5px 0 ;
position : static ;
>
#site-description <
margin : 0 0 15px ;
position : static ;
>
#content <
width : auto ;
float : none ;
margin : 20px 0 ;
>
#sidebar <
width : 100 % ;
float : none ;
margin : 0 ;
>
>
Размер экрана меньше 480px
- html = отключаем регулировку размера шрифта. По умолчанию iPhone увеличивает размер шрифта, для более комфортного чтения. Вы можете это отключить добавив -webkit-text-size-adjust: none;
- main-nav = сбрасываем размер шрифта до 90%.
@media screen and (max-width: 480px) <
html <
-webkit-text-size-adjust : none ;
>
#main-nav a <
font-size : 90 % ;
padding : 10px 8px ;
>
>
Эластичные изображения
Для того, чтобы сделать изображения эластичными, просто добавьте max-width:100% и height:auto . Изображения max-width:100% и height:auto работает в IE7, но не работает в IE8 (да, еще один странный баг). Для исправления нужно добавить width:auto\9 для IE8.
Эластичные встраиваемые видео
Для видео применяем те же правила, как для изображений. По непонятным причинам max-width:100% (для видео) не работает в Safari. Нужно использовать width: 100% .
Initial Scale Meta Tag (iPhone)
По умолчанию iPhone Safari сжимает станицы, что бы вместить в экран. Следующий мета-тег говорит iPhone Safari использовать ширину устройства как ширину окна и отключить.
Финальное Демо
Откроем финальное демо и поизменяем размер экрана, что бы увидеть media queries в действии. Не забудьте проверить в iPhone, iPad, Blackberry (последние версии) и Android телефонах, что бы увидеть мобильную версию.
HTML Responsive Web Design
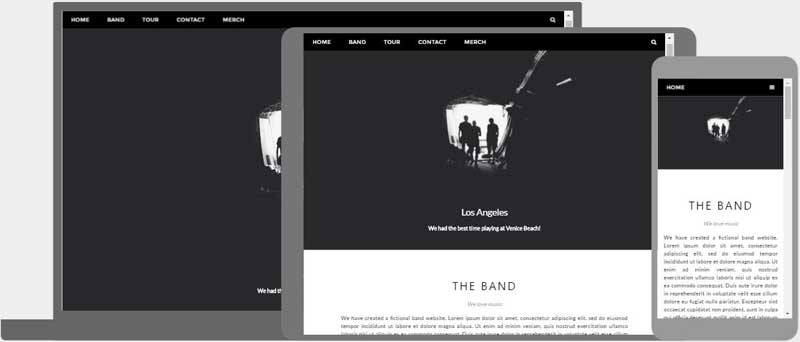
Responsive web design is about creating web pages that look good on all devices!
A responsive web design will automatically adjust for different screen sizes and viewports.
What is Responsive Web Design?
Responsive Web Design is about using HTML and CSS to automatically resize, hide, shrink, or enlarge, a website, to make it look good on all devices (desktops, tablets, and phones):
Setting The Viewport
To create a responsive website, add the following tag to all your web pages:
Example
This will set the viewport of your page, which will give the browser instructions on how to control the page’s dimensions and scaling.
Here is an example of a web page without the viewport meta tag, and the same web page with the viewport meta tag:
Without the viewport meta tag:
With the viewport meta tag:
Tip: If you are browsing this page on a phone or a tablet, you can click on the two links above to see the difference.
Responsive Images
Responsive images are images that scale nicely to fit any browser size.
Using the width Property
If the CSS width property is set to 100%, the image will be responsive and scale up and down:
Example
style=»width:100%;»>
Notice that in the example above, the image can be scaled up to be larger than its original size. A better solution, in many cases, will be to use the max-width property instead.
Using the max-width Property
If the max-width property is set to 100%, the image will scale down if it has to, but never scale up to be larger than its original size:
Example
Responsive Text Size
The text size can be set with a «vw» unit, which means the «viewport width».
That way the text size will follow the size of the browser window:
Hello World
Resize the browser window to see how the text size scales.
Example
Hello World
Viewport is the browser window size. 1vw = 1% of viewport width. If the viewport is 50cm wide, 1vw is 0.5cm.
Media Queries
In addition to resize text and images, it is also common to use media queries in responsive web pages.
With media queries you can define completely different styles for different browser sizes.
Example: resize the browser window to see that the three div elements below will display horizontally on large screens and stack vertically on small screens:
Example
.main float: left;
width: 60%; /* The width is 60%, by default */
>
/* Use a media query to add a breakpoint at 800px: */
@media screen and (max-width: 800px) .left, .main, .right width: 100%; /* The width is 100%, when the viewport is 800px or smaller */
>
>
Tip: To learn more about Media Queries and Responsive Web Design, read our RWD Tutorial.
Responsive Web Page — Full Example
A responsive web page should look good on large desktop screens and on small mobile phones.
Ever heard about W3Schools Spaces? Here you can create your website from scratch or use a template, and host it for free.
Responsive Web Design — Frameworks
All popular CSS Frameworks offer responsive design.
They are free, and easy to use.
W3.CSS
W3.CSS is a modern CSS framework with support for desktop, tablet, and mobile design by default.
W3.CSS is smaller and faster than similar CSS frameworks.
W3.CSS is designed to be independent of jQuery or any other JavaScript library.
W3.CSS Demo
Resize the page to see the responsiveness!
London
London is the capital city of England.
It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
Paris
Paris is the capital of France.
The Paris area is one of the largest population centers in Europe, with more than 12 million inhabitants.
Tokyo
Tokyo is the capital of Japan.
It is the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, and the most populous metropolitan area in the world.
Example
W3Schools Demo
Resize this responsive page!
London
London is the capital city of England.
It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
Paris
Paris is the capital of France.
The Paris area is one of the largest population centers in Europe,
with more than 12 million inhabitants.
Tokyo
Tokyo is the capital of Japan.
It is the center of the Greater Tokyo Area,
and the most populous metropolitan area in the world.
To learn more about W3.CSS, read our W3.CSS Tutorial.
Bootstrap
Another popular CSS framework is Bootstrap:
Example
My First Bootstrap Page
Resize this responsive page to see the effect!
Column 1
Lorem ipsum.
Column 2
Lorem ipsum.
Column 3
Lorem ipsum.
To learn more about Bootstrap, go to our Bootstrap Tutorial.