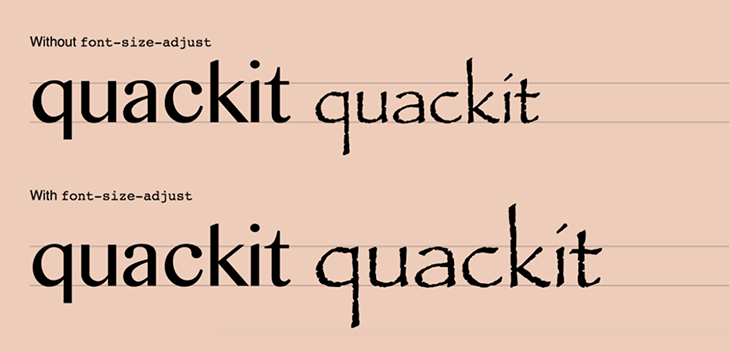- CSS font-size-adjust Property
- Browser Support
- Syntax
- Property Values
- CSS font-size-adjust : How to auto-adjust your font size
- How CSS font-size-adjust works
- Browser compatibility for font-size-adjust
- The CSS font-size property
- The CSS font-size-adjust property
- Over 200k developers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
- Conclusion
- Is your frontend hogging your users’ CPU?
- font-size-adjust
- Syntax
- Values
- Formal definition
CSS font-size-adjust Property
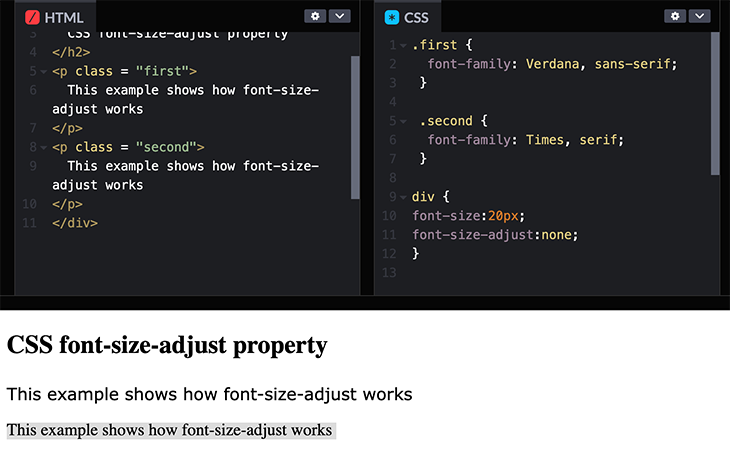
The font-size-adjust property gives you better control of the font size when the first selected font is not available.
When a font is not available, the browser uses the second specified font. This could result in a big change for the font size. To prevent this, use the font-size-adjust property.
All fonts have an «aspect value» which is the size-difference between the lowercase letter «x» and the uppercase letter «X».
When the browser knows the «aspect value» for the first selected font, the browser can figure out what font-size to use when displaying text with the second choice font.
| Default value: | none |
|---|---|
| Inherited: | yes |
| Animatable: | yes. Read about animatable |
| Version: | CSS3 |
| JavaScript syntax: | object.style.fontSizeAdjust=»0.58″ Try it |
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the property.
Syntax
Property Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Defines the aspect value to use |
| none | Default value. No font size adjustment |
| initial | Sets this property to its default value. Read about initial |
| inherit | Inherits this property from its parent element. Read about inherit |
CSS font-size-adjust : How to auto-adjust your font size
In this article, we’ll take a look at how the font-size-adjust attribute helps you auto-adjust your font size. We’ll cover the following topics:
How CSS font-size-adjust works
Developers often employ numerous font families and font sizes on a single webpage for style and readability purposes. A developer might, for example, use the Open Sans typeface for headlines and the Roboto Mono font for the body.
When a font cannot be accessed, the browser falls back on the second font provided, which may cause a significant shift in font size, and, in turn, shift around other parts of our UI. To give a better depiction of this as it would appear when implemented, take a look at the below illustration.
This example compares two typefaces with differing x-heights and demonstrates how the x-height of one may be adjusted to match the x-height of the other using font-size-adjust . Though both examples use the same two fonts, in the first line without font-size-adjust applied, all of the lowercase letters in the first font are much taller than those in the second font.
This is where font-size-adjust comes in handy — in the second line, the attribute adjusts the size of the letters in the second font to match the x-height of the first font’s letters.
font-size-adjust is useful because it determines font readability based on the size of lowercase letters, rather than the size of capital letters, and adjusts the size of lowercase letters to the size of those in the font currently in use.
Using the font-size-adjust attribute can help prevent this from happening by giving you more control over the font size. However, not all typefaces are supported by all browsers, and using unsupported typefaces may make your website look weird, as previously discussed. Let’s take a look at browser compatibility in the next section.
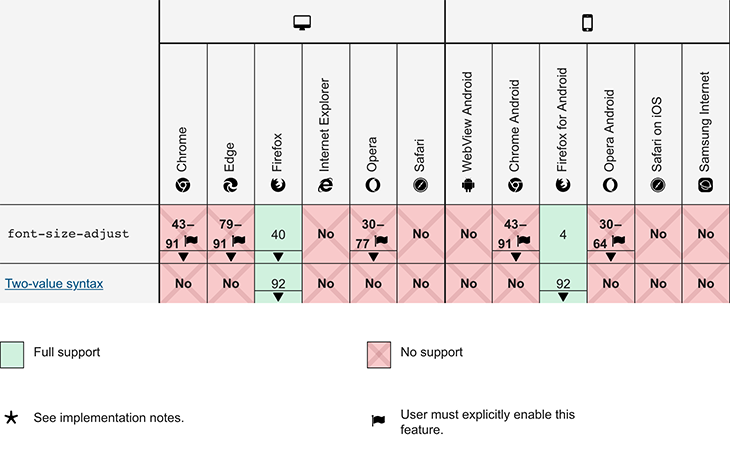
Browser compatibility for font-size-adjust
Before we move into the details, let’s review browser support for the font-size-adjust property. As of writing of this article, the CSS font-size-adjust property is currently only supported by Firefox by default.
Chrome and Opera support this property behind the “Experimental Web Platform Features” flag, which may be activated in chrome:/flags , and ranges from version 43 to 30. The CSS font-size-adjust attribute isn’t currently supported by Edge or Safari.
Now, let’s take a brief look at the CSS font-size property more broadly before diving into the CSS font-size-adjust property.
The CSS font-size property
The font-size CSS property sets the size of the font overall. There are some key things to note about the font-size property:
- When the font-size property is set to a fixed value in em , the size is calculated based on the font size of the parent element
- If other elements are stated in em , changing the font size of one element may impact the font size of others
- When font size is provided as a percentage, it is calculated relative to the font size of the parent element
Here is a sample of the font-size syntax:
/ absolute-size / font-size: medium | xx-small | x-small | small | large | x-large | xx-large; / relative-size / font-size: smaller | larger; / percentage / font-size: 10%; / length / font-size: 5px;
The CSS font-size-adjust property
As we mentioned before, the CSS attribute docs specify that the element’s font size should be adjusted based on the height of lowercase letters, rather than the height of uppercase letters.
When the primary font type cannot be accessed, the CSS font-size-adjust property allows developers to control font size at the component level. In such cases, a font backup is referenced, and the browser switches to display the secondary font.
But if there is a variation in the aspect ratio of the desired original and current fonts, this may cause issues with legibility and accessibility. The CSS font-size-adjust property may be used in situations where we need to retain the text’s legibility while maintaining its aesthetic.
The font-size-adjust syntax is as follows:
number | none | initial | inherit;
- Number : The font-size-adjust property is set to a number
- None : This is the default value
- Initial : Sets the value of this property to its default
- Inherit : The font-size-adjust property is passed down from parent to child
Let’s look at an example. Say that the font-size-adjust property receives a value of 0.5 , which will return a font size that is half the given font size for lowercase letters.
Over 200k developers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Learn more →
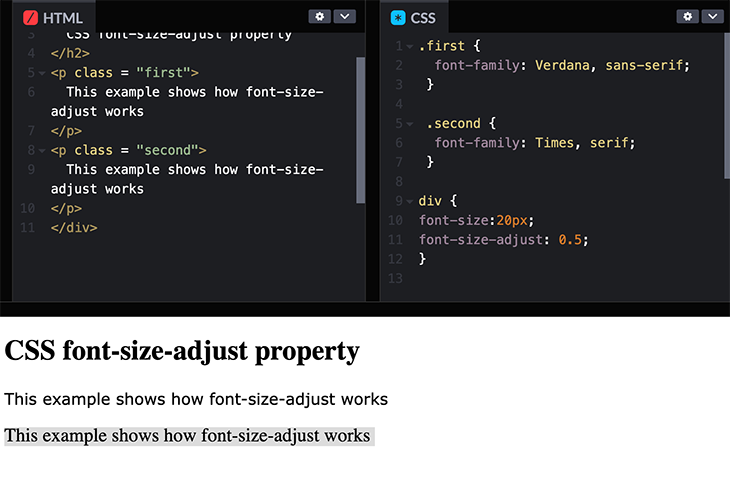
We can also set this property as a number and multiply it by the font-size property to make it compatible with browsers that do not support font-size-adjust . Here’s another example:
font-size: 20px; font-size-adjust: 0.5;
This sets the x-height of the font’s lowercase letters to 20 * 0.5 , which is equal to 10px .
In browsers that do not support font-size-adjust , a 20px font will still be executed when using this method.
Based on the image above, the difference between the two fonts isn’t very obvious. Whereas, if you use none , the predefined font, and its given size:
You can more clearly see that there is a clear difference between these two fonts. The size of both sentences is based on the font-size property, using the predefined font-size.
Conclusion
You should now have a better understanding of what the CSS font-size-adjust property does, why it’s important, and how to include it in your CSS styles.
You can start using this property in your web applications in order to improve legibility and aesthetics. Given that it is only supported by one browser, to avoid size difference due to browser incompatibility, it’s probably still a best practice to pick typefaces with closely comparable ratios.
Thank you, and happy styling.
Is your frontend hogging your users’ CPU?
As web frontends get increasingly complex, resource-greedy features demand more and more from the browser. If you’re interested in monitoring and tracking client-side CPU usage, memory usage, and more for all of your users in production, try LogRocket.https://logrocket.com/signup/
LogRocket is like a DVR for web and mobile apps, recording everything that happens in your web app, mobile app, or website. Instead of guessing why problems happen, you can aggregate and report on key frontend performance metrics, replay user sessions along with application state, log network requests, and automatically surface all errors.
Modernize how you debug web and mobile apps — Start monitoring for free.
font-size-adjust
The font-size-adjust CSS property sets the size of lower-case letters relative to the current font size (which defines the size of upper-case letters).
/* Use the specified font size */ font-size-adjust: none; /* Use a font size that makes lowercase letters half the specified font size */ font-size-adjust: 0.5; /* Two values - added in the Level 5 spec */ font-size-adjust: ex-height 0.5; /* Global values */ font-size-adjust: inherit; font-size-adjust: initial; font-size-adjust: revert; font-size-adjust: revert-layer; font-size-adjust: unset;
The property is useful since the legibility of fonts, especially at small sizes, is determined more by the size of lowercase letters than by the size of capital letters. Legibility can become an issue when the first-choice font-family is unavailable and its replacement has a significantly different aspect ratio (the ratio of the size of lowercase letters to the size of the font).
To use this property in a way that is compatible with browsers that do not support font-size-adjust , it is specified as a number that the font-size property is multiplied by. This means the value specified for the property should generally be the aspect ratio of the first choice font. For example, consider this style sheet:
font-size: 14px; font-size-adjust: 0.5;
It is really specifying that the lowercase letters of the font should be 7px high (0.5 × 14px). This will still produce reasonable results in browsers that do not support font-size-adjust , where a 14px font will be used.
Syntax
Values
Choose the size of the font based only on the font-size property.
ex-height | cap-height | ch-width | ic-width | ic-height
Specifies the font metric to normalize on. Defaults to ex-height . One of:
Normalize the aspect value of the fonts, using the x-height divided by the font size.
Normalize the cap-height of the fonts, using the cap-height by the font size.
Normalize the horizontal narrow pitch of the fonts, using the advance width of «0» (ZERO, U+0030) divided by the font size.
Normalize the horizontal wide pitch of the font, using the advance width of «水» (CJK water ideograph, U+6C34) divided by the font size.
Normalize the vertical wide pitch of the font, using the advance height of «水» (CJK water ideograph, U+6C34) divided by the font size.
Choose the size of the font so that its lowercase letters (as determined by the x-height of the font) are the specified number times the font-size .
The number specified should generally be the aspect ratio (ratio of x-height to font size) of the first choice font-family . This means that the first-choice font, when available, will appear the same size in browsers, whether or not they support font-size-adjust .
0 yields text of zero height (hidden text).