- Sequence (последовательность)
- Адресация элементов
- Сравнение последовательностей
- Проход по элементам
- Количество элементов
- Слияние (конкатенация)
- Повторение
- Рекомендуемые методы
- Python Sequences
- Introduction to Python sequences
- Sequence type vs iterable type
- Standard Python sequence methods
- 1) Counting elements of a Python sequence
- 2) Checking if an item exists in a Python sequence
- 3) Finding the index of an item in a Python sequence
- 4) Slicing a sequence
- 5) Getting min and max items from a Python sequence
- 6) Concatenating two Python sequences
- 7) Repeating a Python sequence
- Summary
Sequence (последовательность)
Последовательности могут быть как изменяемыми, так и неизменяемыми. Размерность и состав созданной однажды неизменяемой последовательности не может меняться, вместо этого обычно создаётся новая последовательность.
Последовательности поддерживают сравнение (обычно производится лексикографически).
Пользовательские последовательности подчиняются Протоколу последовательностей.
Примеры последовательностей в стандартной библиотеке:
Адресация элементов
Доступ к значениям последовательностей производится при помощи индексов — целых чисел, означающих позиций элементов.
Нумерация индексов начинается с 0 (нуля).
Если по указанному индексу значение отсутствует, возбуждается исключение IndexError.
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
my_tuple[0] # 1
my_tuple[10] # IndexError Сравнение последовательностей
При сравнение используется лексикографический порядок, сравниваются два элемента, идущих друг за другом, начиная с первого. Вложенные последовательности одинакового типа сравниваются рекурсивно. Последовательности равны, если их элементы равны.
+py3.0 При лексикографическом сравнении для строк используются номера кодовых точек Юникода.
(1, 2, 3) < (1, 2, 4)
[1, 2, 3] < [1, 2, 4]
'ABC' < 'C' < 'Pascal' < 'Python'
(1, 2, 3, 4) < (1, 2, 4)
(1, 2) < (1, 2, -1)
(1, 2, 3) == (1.0, 2.0, 3.0)
(1, 2, ('aa', 'ab')) < (1, 2, ('abc', 'a'), 4)
# Python 2
[1, 'two'] < ['two', 1] # True
# Python 3
[1, 'two']
Сравнение различных типов внутри последовательности (при помощи > и <) поддерживается, если для типов определены методы сравнения. В противном случае возбуждается TypeError (до +py3.0 порядок был произвольным, типы сравнивались по имени — list < str < tuple и т.д.). Например, численные типы сравниваются по их численному значению, то есть как 0==0.00 .
Проход по элементам
Проход по элементам последовательности производится при помощи for in:
for item in [1, 2, 3]:
print(item) Количество элементов
Количество элементов в последовательности можно получить, используя функцию len().
Слияние (конкатенация)
Конкатенация двух последовательностей производится при помощи + .
a = [3, 2, 1]
b = [4, 5, 6]
a + b # [3, 2, 1, 4, 5, 6] Повторение
Повторение (множение) элементов последовательностей производится при помощи * .
a = [1] * 5
a # [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
b = [1, 2] * 3
b # [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2] Рекомендуемые методы
Пользовательским последовательностям по примеру таковых же из стандартной библиотеки рекомендуется реализовать следующие методы.
| Базовые | __contains__(), __iter__() |
| Для изменяемых последовательностей | append(), count(), extend(), index(), insert(), pop(), remove(), reverse(), sort() |
| Для поддержки слияния и повторения | __add__(), __iadd__(), __imul__(), __mul__(), __radd__(), __rmul__() |
Для перегрузки математических операций (умножение — повторение, а сложение — конкатенация) следует использовать только указанные методы. Прочие методы для работы с числами реализовываться не должны.
Статьи раздела
| list (список) | Список — изменяемая последовательность с упорядоченными элементами. |
| range (диапазон) | Диапазон — неизменяемая последовательность целых чисел. |
| sequence.index | Ищет указанное значение в последовательности. |
| str (строка) | Строка — базовый тип представляющий из себя неизменяемую последовател… |
| tuple (кортеж) | Кортеж — неизменяемая последовательность с упорядоченными элементами. |
| xrange | Диапазон — неизменяемая последовательность целых чисел. |
Python Sequences
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Python sequences and their basic operations.
Introduction to Python sequences
A sequence is a positionally ordered collection of items. And you can refer to any item in the sequence by using its index number e.g., s[0] and s[1] .
In Python, the sequence index starts at 0, not 1. So the first element is s[0] and the second element is s[1] . If the sequence s has n items, the last item is s[n-1] .
Python has the following built-in sequence types: lists, bytearrays, strings, tuples, range, and bytes. Python classifies sequence types as mutable and immutable.
The mutable sequence types are lists and bytearrays while the immutable sequence types are strings, tuples, range, and bytes.
A sequence can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. In a homogeneous sequence, all elements have the same type. For example, strings are homogeneous sequences where each element is of the same type.
Lists, however, are heterogeneous sequences where you can store elements of different types including integer, strings, objects, etc.
In general, homogeneous sequence types are more efficient than heterogeneous in terms of storage and operations.
Sequence type vs iterable type
An iterable is a collection of objects where you can get each element one by one. Therefore, any sequence is iterable. For example, a list is iterable.
However, an iterable may not be a sequence type. For example, a set is iterable but it’s not a sequence.
Generally speaking, iterables are more general than sequence types.
Standard Python sequence methods
The following explains some standard sequence methods:
1) Counting elements of a Python sequence
To get the number of elements of a sequence, you use the built-in len function:
The following example uses the len function to get the number of items in the cities list:
cities = ['San Francisco', 'New York', 'Washington DC'] print(len(cities)) Code language: PHP (php)2) Checking if an item exists in a Python sequence
To check if an item exists in a sequence, you use the in operator:
The following example uses the in operator to check if the ‘New York’ is in the cities list:
cities = ['San Francisco', 'New York', 'Washington DC'] print('New York' in cities)Code language: PHP (php)TrueCode language: PHP (php)To negate the in operator, you use the not operator. The following example checks if ‘New York’ is not in the cities list:
cities = ['San Francisco', 'New York', 'Washington DC'] print('New York' not in cities)Code language: PHP (php)FalseCode language: PHP (php)3) Finding the index of an item in a Python sequence
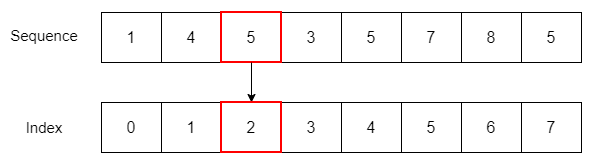
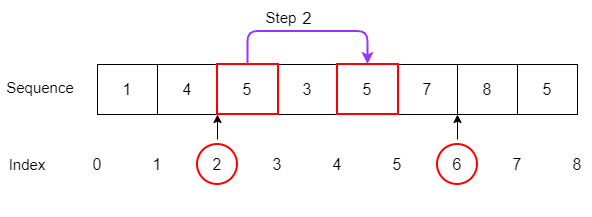
The seq.index(e) returns the index of the first occurrence of the item e in the sequence seq :
seq.index(e)Code language: CSS (css)numbers = [1, 4, 5, 3, 5, 7, 8, 5] print(numbers.index(5)) Code language: PHP (php)The index of the first occurrence of number 5 in the numbers list is 2. If the number is not in the sequence, you’ll get an error:
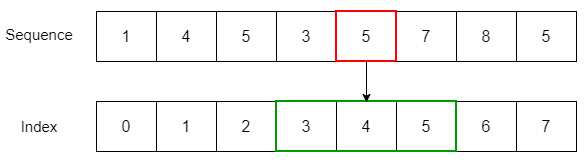
numbers = [1, 4, 5, 3, 5, 7, 8, 5] print(numbers.index(10)) Code language: PHP (php) ValueError: 10 is not in listCode language: PHP (php)To find the index of the first occurrence of an item at or after a specific index, you use the following form of the index method:
seq.index(e, i)Code language: CSS (css)The following example returns the index of the first occurrence of the number 5 after the third index:
numbers = [1, 4, 5, 3, 5, 7, 8, 5] print(numbers.index(5, 3)) Code language: PHP (php)The following form of the index method allows you to find the index of the first occurrence of an item at or after the index i and before index j :
seq.index(e, i, j)Code language: CSS (css)numbers = [1, 4, 5, 3, 5, 7, 8, 5] print(numbers.index(5, 3, 5)) Code language: PHP (php)4) Slicing a sequence
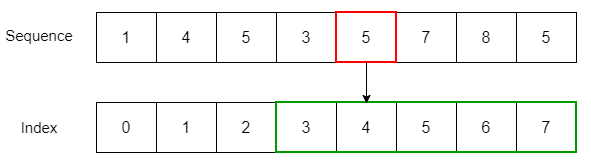
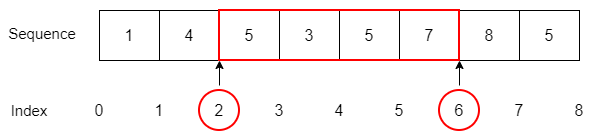
To get the slice from the index i to (but not including) j , you use the following syntax:
seq[i:j]Code language: CSS (css)numbers = [1, 4, 5, 3, 5, 7, 8, 5] print(numbers[2:6])Code language: PHP (php)[5, 3, 5, 7]Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)When you slice a sequence, it’s easier to imagine that the sequence indexes locate between two items like this:
The extended slice allows you to get a slice from i to (but not including j ) in steps of k :
seq[i:j:k]Code language: CSS (css)numbers = [1, 4, 5, 3, 5, 7, 8, 5] print(numbers[2:6:2]) Code language: PHP (php)[5, 5]Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)5) Getting min and max items from a Python sequence
If the ordering between items in a sequence is specified, you can use the built-in min and max functions to find the minimum and maximum items:
numbers = [1, 4, 5, 3, 5, 7, 8, 5] print(min(numbers)) # 1 print(max(numbers)) # 8 Code language: PHP (php)6) Concatenating two Python sequences
To concatenate two sequences into a single sequence, you use the + operator:
The following example concatenates two sequences of strings:
east = ['New York', 'New Jersey'] west = ['San Diego', 'San Francisco'] cities = east + west print(cities)Code language: PHP (php)['New York', 'New Jersey', 'San Diego', 'San Francisco']Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)It’s quite safe to concatenate immutable sequences. The following example appends one element to the west list. And it doesn’t affect the cities sequence:
west.append('Sacramento') print(west) print(cities)Code language: PHP (php)['San Diego', 'San Francisco', 'Sacramento'] ['New York', 'New Jersey', 'San Diego', 'San Francisco']Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)However, you should be aware of concatenations of mutable sequences. The following example shows how to concatenate a list to itself:
city = [['San Francisco', 900_000]] cities = city + city print(cities)Code language: PHP (php)[['San Francisco', 1000000], ['San Francisco', 1000000]]Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)Since a list is mutable, the memory addresses of the first and second elements from the cities list are the same:
print(id(cities[0]) == id(cities[1])) # TrueCode language: PHP (php)In addition, when you change the value from the original list, the combined list also changes:
city[0][1] = 1_000_000 print(cities)Code language: PHP (php)city = [['San Francisco', 900_000]] cities = city + city print(cities) print(id(cities[0]) == id(cities[1])) # True city[0][1] = 1_000_000 print(cities)Code language: PHP (php)[['San Francisco', 900000], ['San Francisco', 900000]] True [['San Francisco', 1000000], ['San Francisco', 1000000]]Code language: CSS (css)7) Repeating a Python sequence
To repeat a sequence a number of times, you use the multiplication operator (*). The following example repeats the string Python three times:
s = 'ha' print(s*3) Code language: PHP (php)