- Python pip: command not found Solution
- pip: command not found
- How to check if pip is installed correctly?
- Installing pip the right way
- Installing pip for Python 2
- How do I check whether a module is installed in Python, and install it if needed?
- Check if pip is installed python
- # Table of Contents
- # Check if a Python package is installed
- # Installing the module if it isn’t already installed
- # Check if a Python package is installed using find_spec
- # Installing the package if it isn’t already installed
- # Checking if the module isn’t installed
- # Additional Resources
- How do I Update PIP to Latest Version & Check if PIP Package is Installed
- How do I Update PIP to Latest Version
- How do you check if a PIP Package is Installed
- Check what PIP modules are Installed through the “PIP list” Command
- Check what PIP modules are Installed through the “PIP freeze” Command
- How to update PIP Modules
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
Python pip: command not found Solution
Pip is a recursive acronym for either “Pip Installs Packages” or “Pip Installs Python.” Alternatively, pip stands for “preferred installer program.” Basically, it is a package manager that allows you to download and install packages. If you try to install packages without pip installed, you will get an error pip: command not found.
In this article, we will look at the cause of this error and possible solutions to fix this error which you are encountering.
pip: command not found
The issue differs based on the environment and the os which you are using. Let’s understand how the pip is packaged into different environments.
bash: pip: command not found
Error Message from DOS command line:
'pip' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
- Linux – If you have installed Python on a Linux environment, the pip does not come with Python, and you need to install pip package manager as a separate package. Hence in Linux, if you try to install a package, you will get a pip: command not found error as there is no pip package installed.
- Mac – On a mac, if you install the latest version of Python3.x, you don’t have to worry about installing it separately. It comes shipped with Python distributable.
- Windows – On windows again, you don’t have to install the pip separately. It comes with Python distributable.
As you already know, Python 2 has reached the end of life, which means it is no longer actively maintained and supported. If you are still using Python 2, then you should consider moving it to Python 3 and it comes with pip3.
How to check if pip is installed correctly?
The first and foremost thing to do is to check if you have already installed pip in your machine. In windows, you can check if the pip is located in the below directory. So just navigate to the directory and do check for pip.exe or pip3.exe files. If it’s not present, then you need to install it.
C:\Users\YOUR_USERNAME\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\Scripts
Note: Replace the YOUR_USERNAME with your actual username.
Installing pip the right way
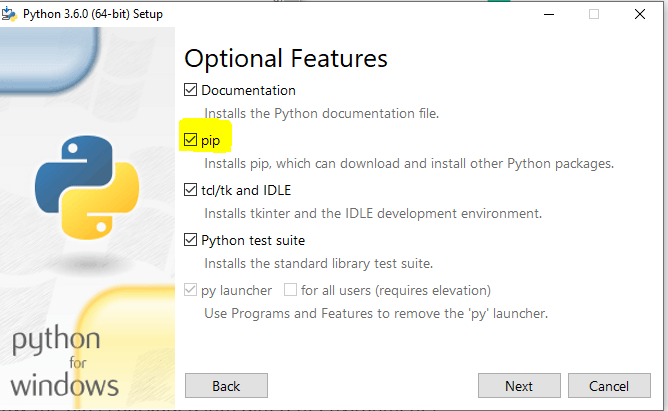
1) On windows, run your Python installer once again and ensure you check the install pip checkbox in the wizard as shown in the below image.
2) On Linux, you can install pip3 by running an apt-get command in your terminal.
sudo apt-get -y install python3-pip
Once you have run this command, you should use the pip3 package manager commands to download the packages.
3) On Mac, pip is bundled with the Python distributable, so you need to re-install Python once again by executing the below command. Once you have re-installed Python 3, you should be able to execute pip commands.
brew install python3
Installing pip for Python 2
If you are still working on Python 2 and want to install an older version of a pip, you can install it by running the below command on your Linux machine.
This command installs the pip command onto your system. If you do not already have easy_install installed, install it using the following Linux command:
sudo apt-get install python-setuptools
How do I check whether a module is installed in Python, and install it if needed?
Warning: It is highly recommended to install python-modules using official Ubuntu repository only and not to use the pip method as superuser(i.e., as root or using sudo ). In some cases it may leave your system unusable by breaking system python.
Like in your answer math module exists and for numby the traceback didnt appear and for echo $? output was 0, Does it mean numpy is also present in my system?
In case you don’t have the module numpy how will you import it? When we do the coding we call the import statement by from numpy import *, will it install the module ? If not how will we install a new module?
It will be a septate question how to install a module. Need different packages for different module. For example to install vpython you need to install it as sudo apt-get install python-visual libgtkglextmm-x11-1.2-dev
don’t use sudo pip ; it may break system python. Use apt-get to install packages for system python. You could use pip —user option or virtualenv to install Python packages for yourself.
In case we do not want to unwantedly import a module in question (which would happen in a try statement) we can make use of sys.modules to test modules that are installed and were imported before.
In the python shell issue:
Then test for installed modules:
>>> 'numpy' in sys.modules True >>> 'scipy' in sys.modules False Note that only those modules that were imported before give True on this test, all other modules (even if installed) result in False.
Another alternative to try an import statement in the python console is calling the inbuilt help() function. This will not give a documentation for non-installed modules, e.g.
>>> help('scipy') no Python documentation found for 'scipy' The output of very long help documents of installed modules can be interrupted with Q .
Now to install missing modules it is recommended to use the Ubuntu package management (and not the Python pip way) because we need root access and also to prevent messing up our heavily Python-dependend system. For the module in question this would e.g. be:
sudo apt-get install python-scipy ## for Python2 sudo apt-get install python3-scipy ## for Python3 After installation we then can add them to the sys.modules dictionary by importing them once.
Check if pip is installed python
Last updated: Feb 23, 2023
Reading time · 3 min
# Table of Contents
# Check if a Python package is installed
To check if a Python package is installed:
- Import the package in a try block.
- Use an except block to handle the potential ModuleNotFoundError .
- If the try block runs successfully, the module is installed.
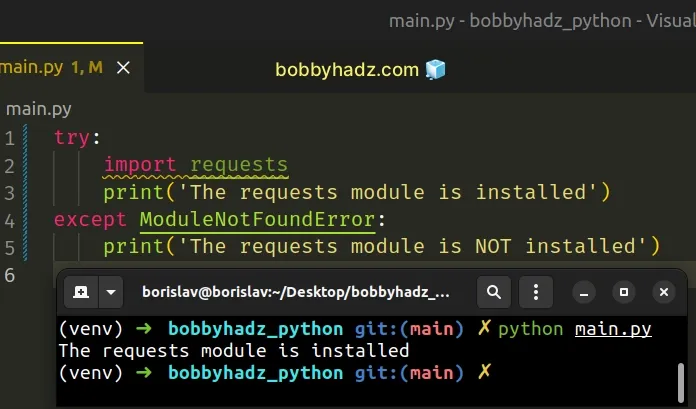
Copied!try: import requests print('The requests module is installed') except ModuleNotFoundError: print('The requests module is NOT installed')
We used a try/except block to check if a module is installed.
If the try block doesn’t raise an exception, the module is installed.
If the module isn’t installed, a ModuleNotFoundError error is raised and the except block runs.
# Installing the module if it isn’t already installed
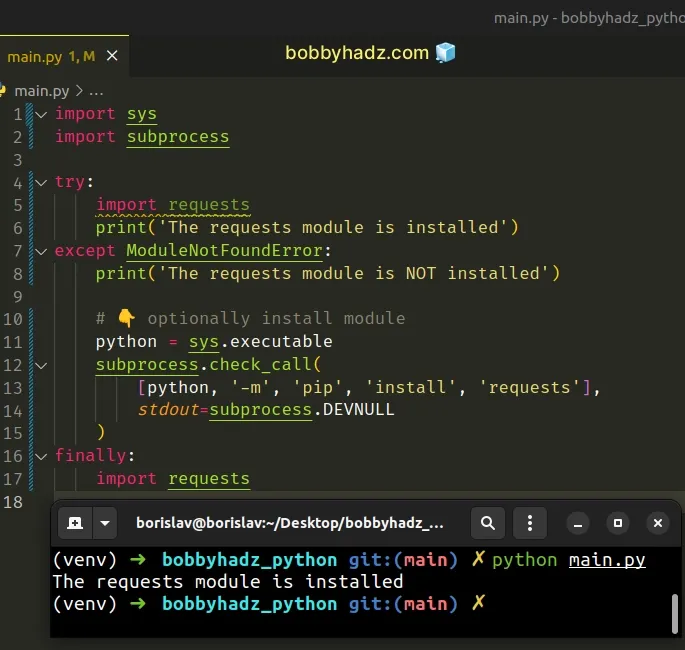
You can also extend the try/except statement to install the module if it isn’t installed.
Copied!import sys import subprocess try: import requests print('The requests module is installed') except ModuleNotFoundError: print('The requests module is NOT installed') # 👇️ optionally install module python = sys.executable subprocess.check_call( [python, '-m', 'pip', 'install', 'requests'], stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL ) finally: import requests
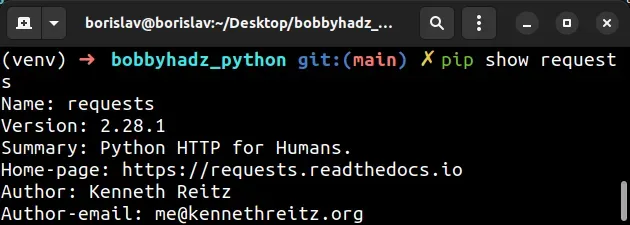
If you need to check if a package is installed using pip , use the pip show command.
The pip show module_name command will either state that the package is not installed or show a bunch of information about the package, including the location where the package is installed.
You can also use the following one-liner command.
Copied!python -c 'import pkgutil; print(1 if pkgutil.find_loader("module_name") else 0)'
Make sure to replace module_name with the actual name of the module you are checking for.
The command returns 1 if the module is installed and 0 if it isn’t but this can be easily adjusted.
# Check if a Python package is installed using find_spec
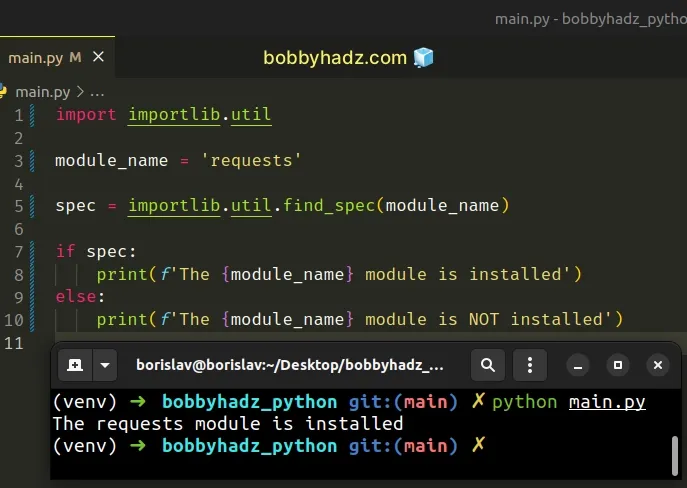
An alternative approach is to use the importlib.util.find_spec method.
The find_spec() method will return a spec object if the module is installed, otherwise, None is returned.
Copied!import importlib.util module_name = 'requests' spec = importlib.util.find_spec(module_name) if spec: print(f'The module_name> module is installed') else: print(f'The module_name> module is NOT installed')
The importlib.util.find_spec method finds the spec for a module.
The spec for a module is a namespace containing the import-related information used to load the module.
If no spec is found, the method returns None.
# Installing the package if it isn’t already installed
You can optionally install the package if it isn’t already installed.
Copied!import importlib.util import sys import subprocess module_name = 'requests' spec = importlib.util.find_spec(module_name) if spec: print(f'The module_name> module is installed') else: print(f'The module_name> module is NOT installed') # 👇️ optionally install the module if it's not installed python = sys.executable subprocess.check_call( [python, '-m', 'pip', 'install', 'requests'], stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL )
# Checking if the module isn’t installed
If you need to check if the module isn’t installed, check if the spec variable stores a None value.
Copied!import importlib.util import sys import subprocess module_name = 'requests' spec = importlib.util.find_spec(module_name) if spec is None: print(f'The module_name> module is NOT installed') # 👇️ optionally install the module if it's not installed python = sys.executable subprocess.check_call( [python, '-m', 'pip', 'install', 'requests'], stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL ) print(f'The module_name> module is now installed')
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I’d use the try/except statement because I find it quite direct and easy to read.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How do I Update PIP to Latest Version & Check if PIP Package is Installed
You might be familiar with the term package manager if coming from the programming world. In Linux distributions, multiple package management tools are used to install, update and remove software packages from the particular repositories.
Like other popular package managers such as npm for JavaScript, a gem for Ruby, the Pip is for Python.
In 2008, Ian Biking introduced a management tool named “pyinstall” to install python packages and distributions. Keep in mind that Biking has also developed the “virtualenv package.” Later, pyinstall changed to Pip Installs Packages after receiving many suggestions.
The PIP is a cross-platform, written in Python to install and manage Python packages from the Python Package Index and from additional libraries (local and remote) that are not part of standard repositories.
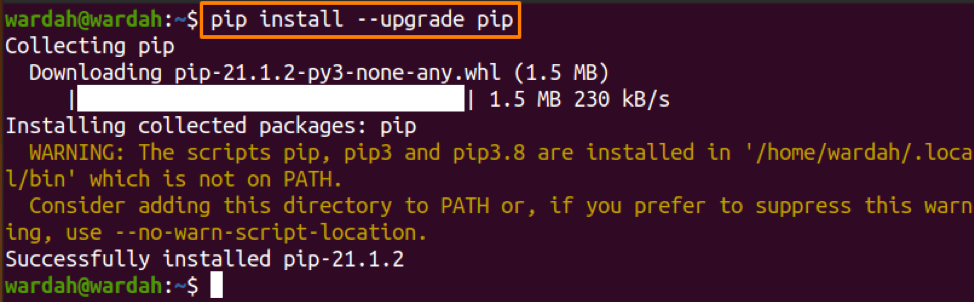
How do I Update PIP to Latest Version
To upgrade the PIP package, the command is quite simple. Type the following command in the terminal:
How do you check if a PIP Package is Installed
To check if pip is already available on the system, the simplest way is to use the version option, and it will show the current version of the PIP package.
So, open the terminal and type:
There are two approaches to check the installed PIP modules:
- Through the “pip list” command
- Through the “pip freeze” command
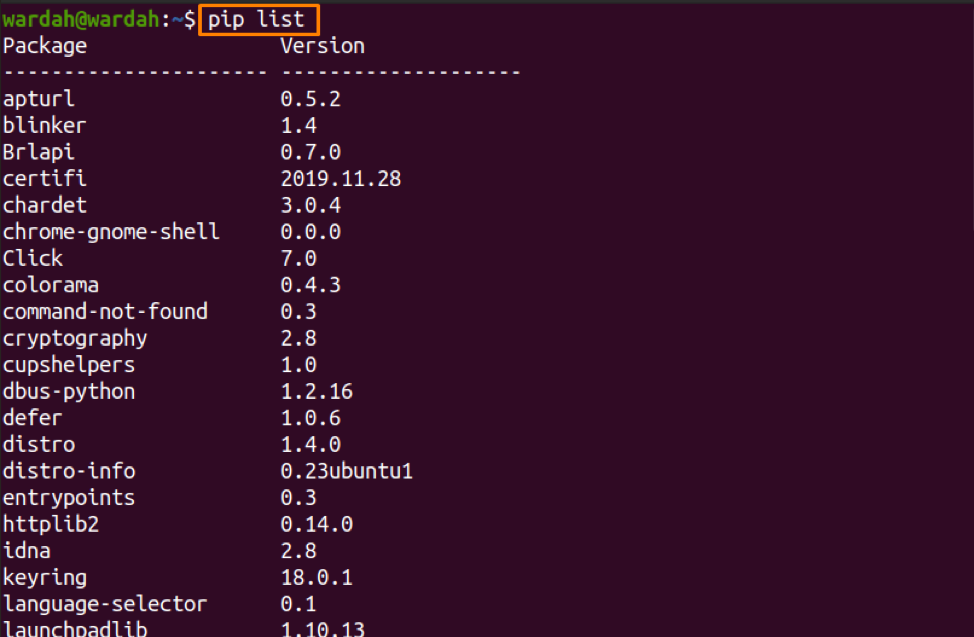
Check what PIP modules are Installed through the “PIP list” Command
The list option will display the list of all the installed modules, including their versions on the system:
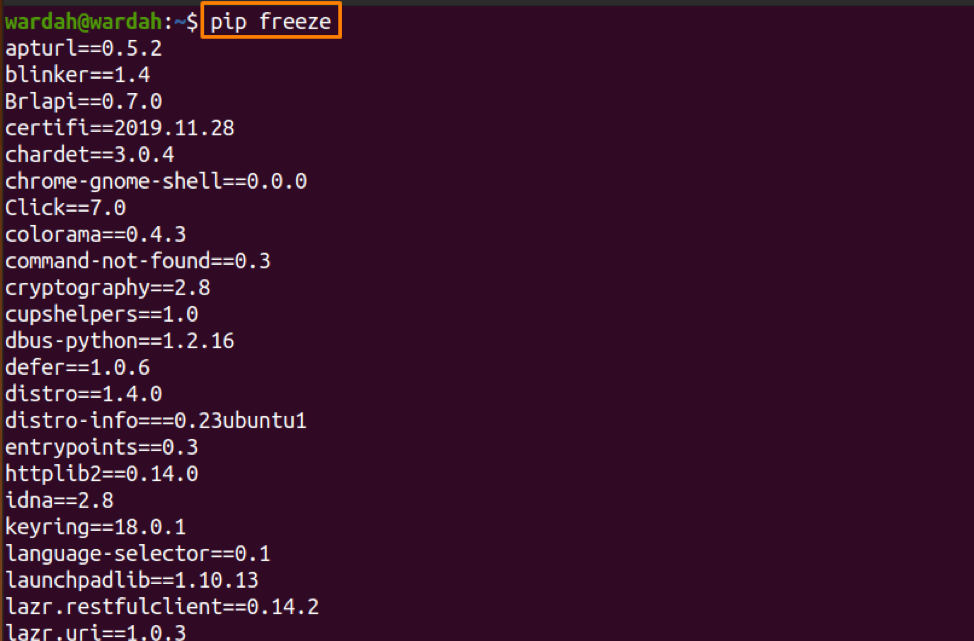
Check what PIP modules are Installed through the “PIP freeze” Command
The “PIP freeze” command is another way to find how many modules have been installed using the PIP package. To get it, type:
How to update PIP Modules
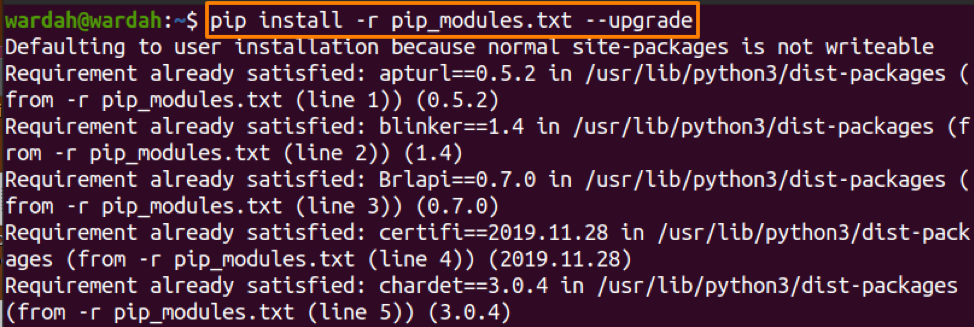
To update all the PIP modules, firstly redirect all the modules name to a text file using the “Freeze” command:
And now, run the following command to update all of them:
Conclusion
The PIP is the package management tool for Python development. Almost all the Python modules with the oldest to latest versions can be downloaded using the PIP package management system.
We have learned how to upgrade the PIP package with all of its modules to the latest version and check the availability of all the installed modules using the “pip list” and “pip freeze” commands.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.