- Securing Spring Boot REST API with Basic Auth
- Использование Basic Authentication с RestTemplate в Spring
- 2. Настройка RestTemplate
- 3. Ручное управление HTTP-заголовком Authorization
- 4. Автоматическое управление HTTP-заголовком Authorization
- 5. Зависимости Maven
- 6. Заключение
- Basic Auth with Spring Security
Securing Spring Boot REST API with Basic Auth
Learn to use basic authentication to secure the REST APIs created in a Spring boot application. The secured API will ask for user authentication credentials before giving access to the API response.
The simplest way to add all required jars is to add the latest version of spring-boot-starter-security dependency.
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-security 2. Configure Spring Security
To enable authentication and authorization support, we can configure the utility class WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter (deprecated). It helps in requiring the user to be authenticated prior to accessing any configured URL (or all URLs) within our application. In the following configuration, we are using httpBasic() which enables basic authentication. We are also configuring the in-memory authentication manager to supply a username and password.
@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter < @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception < http .csrf().disable() .authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .httpBasic(); >@Autowired public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception < auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("admin") .password("password") .roles("ROLE_USER"); > >Starting Spring Boot 2.7.0, WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter is deprecated. We can rewrite the above basic auth configuration in the latest versions as follows:
@Configuration public class BasicAuthWebSecurityConfiguration < @Autowired private AppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint; @Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception < http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/public").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .httpBasic() .authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint); return http.build(); >@Bean public InMemoryUserDetailsManager userDetailsService() < UserDetails user = User .withUsername("user") .password(passwordEncoder().encode("password")) .roles("USER_ROLE") .build(); return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user); >@Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() < return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(8); >>3. Basic Authentication Demo
@RestController @RequestMapping(path = "/employees") public class EmployeeController < @Autowired private EmployeeDAO employeeDao; @GetMapping(path="/", produces = "application/json") public Employees getEmployees() < return employeeDao.getAllEmployees(); >>3.2. Accessing the API without ‘authorization‘ Header
3.3. With ‘authorization‘ Header
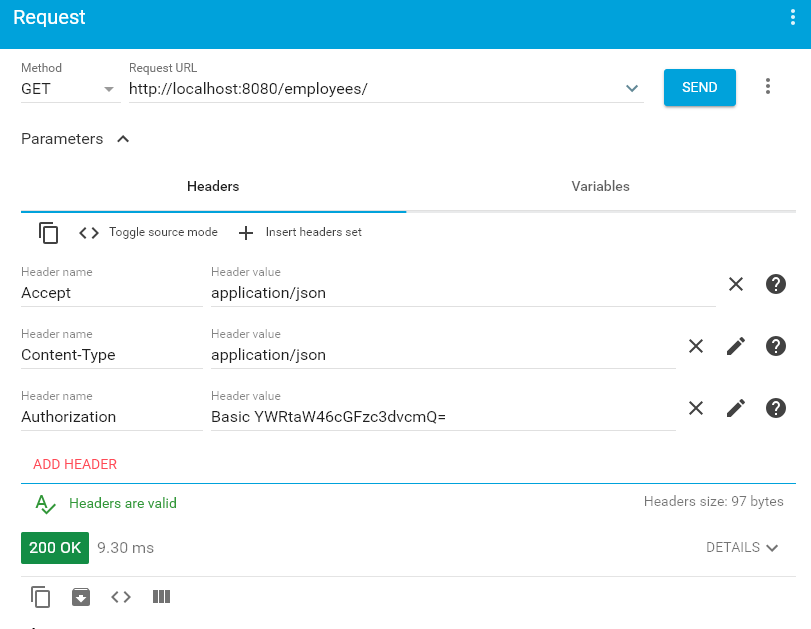
Upon passing authorization request header with encoded basic-auth user name and password combination, we will be able to access the rest api response. Access rest api at URL: HTTP GET http://localhost:8080/employees/
3.4. Generate Basic Auth Encoding
Browser apI testing tools are able to generate the base-64 encoded token by themselves using the plain username and password. But if we need to generate the encoded token ourselves to pass the token programmatically, then we can use the following code that uses the java.util.Base64 class.
String encoding = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString((user + ":" + password).getBytes()); String authHeader = "Basic " + encoding;String encoding = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString((user + ":" + password).getBytes()); HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/api-url"); httpPost.setHeader(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION, "Basic " + encoding); HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost); HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();- The first step is to include required dependencies e.g. spring-boot-starter-security.
- The second step is to configure WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter or SecurityFilterChain and add authentication details.
Использование Basic Authentication с RestTemplate в Spring
В этой статье рассмотрим, как использовать Spring’овый RestTemplate для работы с RESTful-сервисами, защищенными Basic Authentication.
После настройки RestTemplate для работы с Basic Authenticatio n все запросы будут содержать учетные данные, необходимые для выполнения процесса аутентификации. Данные для аутентификации кодируются и записываются в HTTP-заголовок Authorization , который выглядит следующим образом:
Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ==2. Настройка RestTemplate
Для получения RestTemplate в контексте Spring, достаточно объявить его как бин. Но Basic Authentication требует ручной конфигурации, поэтому будем использовать FactoryBean :
@Component public class RestTemplateFactory implements FactoryBean, InitializingBean < private RestTemplate restTemplate; public RestTemplate getObject() < return restTemplate; >public Class getObjectType() < return RestTemplate.class; >public boolean isSingleton() < return true; >public void afterPropertiesSet() < HttpHost host = new HttpHost("localhost", 8082, "http"); restTemplate = new RestTemplate( new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactoryBasicAuth(host)); >>Параметры host и port обычно зависят от окружения: у клиента должна быть возможность определять один набор значений, например, для интеграционного тестирования, а другой для продакшена. Эти значения можно задавать через файлы свойств.
3. Ручное управление HTTP-заголовком Authorization
Заголовок Authorization можно добавить вручную:
HttpHeaders createHeaders(String username, String password)< return new HttpHeaders() >; >Отправить запрос также просто:
restTemplate.exchange (uri, HttpMethod.POST, new HttpEntity(createHeaders(username, password)), clazz);4. Автоматическое управление HTTP-заголовком Authorization
В Spring 3.0 и 3.1, а теперь и в 4.x встроена хорошая поддержка библиотек Apache HTTP:
- В Spring 3.0 CommonsClientHttpRequestFactory интегрирован с ныне устаревшим HttpClient 3.x.
- В Spring 3.1 появилась поддержка текущего HttpClient 4.x через HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory (JIRA SPR-6180).
- В Spring 4.0 появилась поддержка асинхронности через HttpComponentsAsyncClientHttpRequestFactory .
Давайте начнем настройку с HttpClient 4 и Spring 4.
Для RestTemplate потребуется фабрика HTTP-запросов, поддерживающая Basic Authentication. Однако напрямую использовать существующий HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory непросто, поскольку RestTemplate не очень хорошо поддерживает HttpContext — важной части решения. Поэтому нам понадобится создать подкласс HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory и переопределить метод createHttpContext :
public class HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactoryBasicAuth extends HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory < HttpHost host; public HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactoryBasicAuth(HttpHost host) < super(); this.host = host; >protected HttpContext createHttpContext(HttpMethod httpMethod, URI uri) < return createHttpContext(); >private HttpContext createHttpContext() < AuthCache authCache = new BasicAuthCache(); BasicScheme basicAuth = new BasicScheme(); authCache.put(host, basicAuth); BasicHttpContext localcontext = new BasicHttpContext(); localcontext.setAttribute(HttpClientContext.AUTH_CACHE, authCache); return localcontext; >>При создании HttpContext мы добавляем поддержку Basic Authentication. Как видно, упреждающая Basic Authentication с помощью HttpClient 4.x немного обременительна. Информация об аутентификации кэшируется, но настроить вручную этот кэш аутентификации сложно и не интуитивно.
Далее просто добавляем BasicAuthorizationInterceptor в RestTemplate:
restTemplate.getInterceptors().add( new BasicAuthorizationInterceptor("username", "password"));restTemplate.exchange( "http://localhost:8082/spring-security-rest-basic-auth/api/foos/1", HttpMethod.GET, null, Foo.class);Подробнее о том, как обеспечить безопасность самого REST-сервиса читайте в этой статье.
5. Зависимости Maven
Нам потребуются зависимости Maven для самого RestTemplate и библиотеки HttpClient:
org.springframework spring-webmvc 5.0.6.RELEASE org.apache.httpcomponents httpclient 4.5.3 Если мы решим создавать HTTP-заголовок Authorization вручную, то нам также потребуется дополнительная библиотека для поддержки кодирования:
commons-codec commons-codec 1.10 6. Заключение
Большинство информации, которую можно найти по RestTemplate и безопасности, все еще не учитывает текущие релизы HttpClient 4.x, даже несмотря на то, что ветка 3.x устарела и Spring’ом не поддерживается. В этой статье мы немного восполнили этот пробел, описав, как настроить Basic Authentication для RestTemplate, и использовать его для запросов к защищенному REST API.
Полный пример кода с RESTful-сервисом вы можете найти на Github.
Все разработчики проходят одинаковый путь в развитии. Приглашаем всех желающих на demo-занятие «Послание про архитектуру приложений самому себе в прошлое», на котором преподаватель OTUS Виталий Куценко расскажет, как избежать нескольких ошибок, которые могут сильно усложнить развитие приложения. Регистрация по ссылке.
Basic Auth with Spring Security
Learn to configure basic authentication in an application secured with Spring security.
Basic authentication is often used with stateless clients who pass their credentials on each request. It’s quite common to use it in combination with form-based authentication where an application is used through both a browser-based user interface and as a webservice. However, basic authentication transmits the password as plain text so it should only really be used over an encrypted transport layer such as HTTPS.
Because a basic authentication header has to be sent with each HTTP request, the web browser needs to cache the credentials for a reasonable period to avoid constant prompting the user for the username and password. Caching policy differs between browsers.
The client sends HTTP requests with the Authorization header that contains the word Basic word followed by a space and a base64-encoded string username:password .
For example, to authorize as user / password the client would send:
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==2. Default Basic Auth Configuration
The security-related packages and classes are part of the spring security module so let us start with importing the module, first.
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-security The simplest possible solution to implement basic HTTP authentication is to use “ http-basic ” tag in spring security configuration file like this.
The equivalent Java configuration is:
@Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception
The above configuration will force the user to authenticate before accessing any webpage or any other resource in our application.
Interesting thing is that we do not need to create any login page or session management mechanism. The browser will present a login box before the user on our behalf. And because each request contains authentication information just like in HTTP stateless mechanism, we do not need to maintain the session also.
By default, spring will create a user with username “ user ” and generated password is printed in the console. It can be used to authenticate into the application.
Using generated security password: 38b2815c-9943-4b94-b5b6-7adcd5700d103. Custom Basic Auth Configuration
In the following configuration, we have customized a few things:
- We are using InMemoryUserDetailsManager to configure a user (user:password) in place of the default user. We can create as many users as we want, with required authorities assigned to each user.
- Configured the default password encoder to BCryptPasswordEncoder .
- Secured all URLs, except ‘/public ‘ that is allowed to all.
The equivalent Java configuration is:
@Configuration public class BasicAuthWebSecurityConfiguration < @Autowired private AppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint; @Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception < http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/public").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .httpBasic() .authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint); return http.build(); >@Bean public InMemoryUserDetailsManager userDetailsService() < UserDetails user = User .withUsername("user") .password("$2a$10$dXJ3SW6G7P50lGmMkkmwe.20cQQubK3.HZWzG3YB1tlRy.fqvM/BG") .roles("USER_ROLE") .build(); return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user); >@Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() < return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(8); >> 4. Custom BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint
The authentication entry points are used by the ExceptionTranslationFilter to commence authentication. By default, the BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint returns a full page for a 401 Unauthorized response back to the client.
To customize the default authentication error page used by basic auth, we can extend the BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint class. Here we can set the realm name and well as the error message sent back to the client.
@Component public class AppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint extends BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint < @Override public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authEx) throws IOException < response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=" + getRealmName() + ""); response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED); PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter(); writer.println("HTTP Status 401 - " + authEx.getMessage()); >@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() < setRealmName("howtodoinjava"); super.afterPropertiesSet(); >>Start the server and load any non-protected URL in the browser. A login window appears. Please note that it is browser generated login box and the application has only provided relevant headers to the browser.
Enter the incorrect username and password. This will make the browser again present the cleared login box or it will show the error page in some cases like this.
When we enter the correct username and password, the correct response is loaded in the browser
To authenticate using basic auth, for accessing a resource is unit tests, we can use the MockMvcRequestBuilders.with() method when using MockMvc.
@SpringBootTest( webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK, classes = < BasicAuthWebSecurityConfiguration.class, AppBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint.class, AppController.class >) @AutoConfigureMockMvc class BasicAuthTest < @Autowired private MockMvc mvc; @Test void expectOKResponse_WhenAccessNotSecuredURL() throws Exception < ResultActions result = mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/public")) .andExpect(status().isOk()); >@Test void expectUnauthorizedUser_WhenPasswordIsWrong() throws Exception < ResultActions result = mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/") .with(httpBasic("user","wrong-password"))) .andExpect(status().isUnauthorized()); >@Test void expectOKResponse_WhenPasswordIsCorrect() throws Exception < ResultActions result = mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/") .with(httpBasic("user", "password"))) .andExpect(content().string("Hello World !!")); >>In this tutorial, we learned about the default basic authentication commissioned by the Spring security module. We also learned to customize and configure various components involved in the basic authentication including password encoding and custom username and passwords.