- background
- Try it
- Constituent properties
- Syntax
- Values
- Accessibility concerns
- Formal definition
- Formal syntax
- Examples
- Setting backgrounds with color keywords and images
- HTML
- CSS
- Result
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- MDN
- Support
- Our communities
- Developers
- How to Remove Background Color in CSS?
- Method 1: Remove Existing Background Color by Making it Transparent
- Heading with yellow background
- Method 2: Remove Existing Background Color Using background: none
- Heading with yellow background
- background-color: transparent OR background: none Which One Should You Use?
- Conclusion
- Related posts:
- background-color
- Синтаксис
- Значения
- Объектная модель
- Браузеры
background
The background shorthand CSS property sets all background style properties at once, such as color, image, origin and size, or repeat method. Component properties not set in the background shorthand property value declaration are set to their default values.
Try it
Constituent properties
This property is a shorthand for the following CSS properties:
Syntax
/* Using a */ background: green; /* Using a and */ background: url("test.jpg") repeat-y; /* Using a and */ background: border-box red; /* A single image, centered and scaled */ background: no-repeat center/80% url("../img/image.png"); /* Global values */ background: inherit; background: initial; background: revert; background: revert-layer; background: unset;
The background property is specified as one or more background layers, separated by commas.
The syntax of each layer is as follows:
- Each layer may include zero or one occurrences of any of the following values:
- The value may only be included immediately after , separated with the ‘/’ character, like this: » center/80% «.
- The value may be included zero, one, or two times. If included once, it sets both background-origin and background-clip . If it is included twice, the first occurrence sets background-origin , and the second sets background-clip .
- The value may only be included in the last layer specified.
Values
See background-clip and background-origin . Default: border-box and padding-box respectively.
See background-color . Default: transparent .
The following three lines of CSS are equivalent:
background: none; background: transparent; background: repeat scroll 0% 0% / auto padding-box border-box none transparent;
Accessibility concerns
Browsers do not provide any special information on background images to assistive technology. This is important primarily for screen readers, as a screen reader will not announce its presence and therefore convey nothing to its users. If the image contains information critical to understanding the page’s overall purpose, it is better to describe it semantically in the document.
Formal definition
- background-image : none
- background-position : 0% 0%
- background-size : auto auto
- background-repeat : repeat
- background-origin : padding-box
- background-clip : border-box
- background-attachment : scroll
- background-color : transparent
- background-position : refer to the size of the background positioning area minus size of background image; size refers to the width for horizontal offsets and to the height for vertical offsets
- background-size : relative to the background positioning area
- background-image : as specified, but with url() values made absolute
- background-position : as each of the properties of the shorthand:
- background-position-x : A list, each item consisting of: an offset given as a combination of an absolute length and a percentage, plus an origin keyword
- background-position-y : A list, each item consisting of: an offset given as a combination of an absolute length and a percentage, plus an origin keyword
- background-color : a color
- background-image : discrete
- background-clip : a repeatable list of
- background-position : a repeatable list of
- background-size : a repeatable list of
- background-repeat : discrete
- background-attachment : discrete
Formal syntax
background =
[ # , ]?=
||
[ / ]? ||
||
||
||
=
||
||
[ / ]? ||
||
||
||
=
|
none=
[ left | center | right | top | bottom | ] |
[ left | center | right | ] [ top | center | bottom | ] |
[ center | [ left | right ] ? ] && [ center | [ top | bottom ] ? ]=
[ | auto ] |
cover |
contain=
repeat-x |
repeat-y |
[ repeat | space | round | no-repeat ]=
scroll |
fixed |
local=
border-box |
padding-box |
content-box=
|=
|=
url( * ) |
src( * )Examples
Setting backgrounds with color keywords and images
HTML
p class="topbanner"> Starry skybr /> Twinkle twinklebr /> Starry sky p> p class="warning">Here is a paragraphp> p>p>
CSS
.warning background: pink; > .topbanner background: url("starsolid.gif") #99f repeat-y fixed; >Result
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on Jul 18, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
MDN
Support
Our communities
Developers
Visit Mozilla Corporation’s not-for-profit parent, the Mozilla Foundation.
Portions of this content are ©1998– 2023 by individual mozilla.org contributors. Content available under a Creative Commons license.How to Remove Background Color in CSS?
In CSS, if we want to set the background color of an element, we use the background-color property. For example, background-color: red; sets the element’s background color to red, background-color: yellow; to the yellow background, and so on.
But, there may be situations where an element already has some background color and you want to remove it now. For example, you are working on an old project which has a really bad color scheme and you want to change things now.
In this article, I will explain both methods in detail and also some key points to remember while doing this.
Method 1: Remove Existing Background Color by Making it Transparent
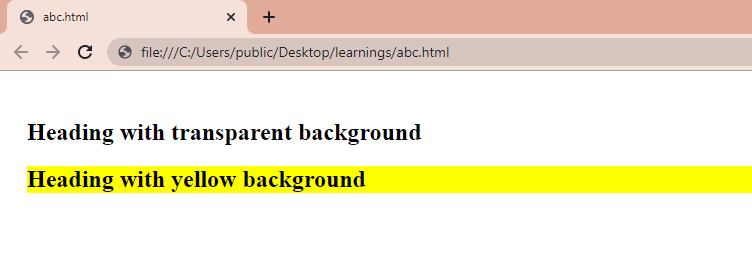
The simplest way to remove any existing background color from an element is to make it transparent. When you make the background color of an element transparent, it will not be visible, doesn’t matter what background color have you applied to the element.
Let’s say we have two subheadings () in our HTML document.
Heading with yellow background
Now, we want don’t to keep any background color on the first subheading i.e. subheading with class=»no-background» .
To achieve that, we can set its background-color property to transparent . This will make the existing background color fully transparent and it will look like there is no background color applied to the element.
/* Apply yellow background color on all subheadings */ h2 < background-color: yellow; >/* Make background color fully transpaernt */ .no-background
Below is the outcome of the above code:
As you can see from the above image, the background color of the first subheading is not visible because we have set its background-color property to transparent .
Method 2: Remove Existing Background Color Using background: none
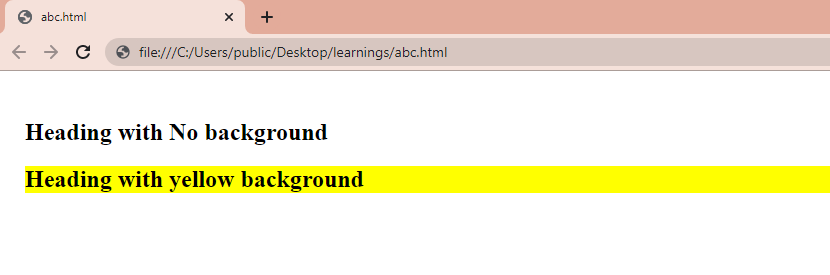
The second method to remove the background color of an element is to set its background property to none .
When you set the background property of an element to none , it means that no background color or image will be applied to the element.
If there is any existing background color applied to the element and you set the background property to none, that existing background color will be completely removed from the element i.e. all existing background colors and images will be overridden by the value none .
Let’s take the same example again, and see if it works:
Heading with yellow background
Now, set the background property to none to remove the existing background color from the first subheading:
/* Apply yellow background color on all subheadings */ h2 < background-color: yellow; >/* Remove background color completely */ .no-background
… And here is the outcome of the above code:
Bingo! the background color is completely removed from the first subheading.
background-color: transparent OR background: none Which One Should You Use?
In the above two examples, we saw that both methods can remove the existing background color from an element. Now, the biggest question arises, which approach should you choose?
The answer depends on your requirements.
If you want to remove only the existing background color of the element, you should choose the first approach i.e. apply background-color: transparent; .
This is because, when you set the background-color property to transparent , only the element’s background color is affected, the background images remain the same.
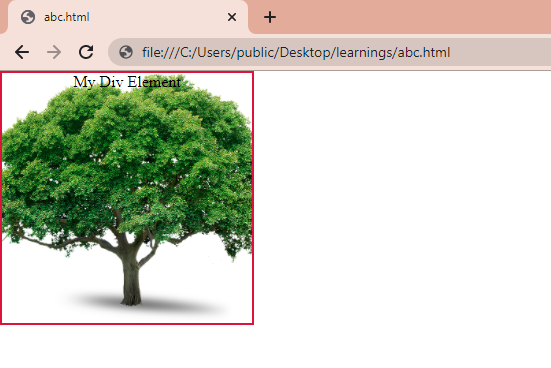
To explain this, let’s take an example, which has a div element with a yellow background color and a background image:
And here is the CSS applied to it:
This is how it is looking after applying the above CSS:
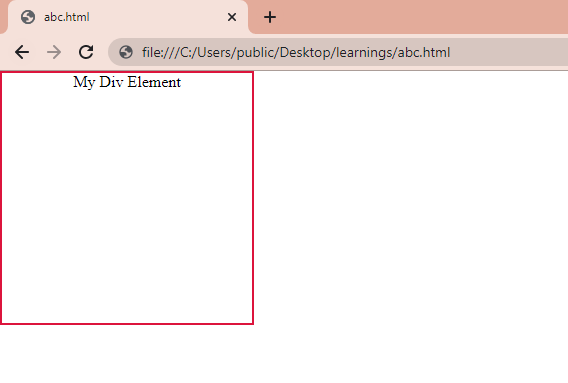
Now, if we use the background-color: transparent; to remove its background color, it will only remove its yellow background color, not the background image. See the following image:
But, if we use the background: none; to remove its background color, its background color and background image both will be removed. This is because background: none; overrides all existing background properties. See the result in the following image:
I think now you got the answer when you should choose which approach.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned how we can remove the existing background color from an element.
To remove the existing background color of an element, you have two approaches. First, make the existing background color transparent by setting the background-color property to transparent .
Second, completely remove the background color from the element by setting its background property to none .
Related posts:
background-color
Определяет цвет фона элемента. Хотя это свойство не наследует свойства своего родителя, из-за того, что начальное значение устанавливается прозрачным, цвет фона дочерних элементов совпадает с цветом фона родительского элемента.
Синтаксис
background-color: | transparent | inherit
Значения
transparent Устанавливает прозрачный фон. inherit Наследует значение родителя.
HTML5 CSS2.1 IE Cr Op Sa Fx
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diem nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut lacreet dolore magna aliguam erat volutpat.
В данном примере для элементов веб-страницы применяется три различных способа задания фонового цвета. Результат примера показан на рис. 1.
Рис. 1. Применение background-color
Объектная модель
[window.]document.getElementById(» elementID «).style.backgroundColorБраузеры
Internet Explorer до версии 7.0 включительно не поддерживает значение inherit .