- Run python script in virtual environment on startup
- How to Run Python Script at Startup in Ubuntu
- Prerequisites
- Running a Python Script at Startup in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Create Your Python Script
- Как поставить на автозапуск python скрипт в linux?
- Войдите, чтобы написать ответ
- Экспорт почты из Exchange Online (office365)?
- .py script to run at the startup [duplicate]
- 2 Answers 2
Run python script in virtual environment on startup
I would like to start a python script from a virtual environment on startup. I have searched the whole forum and other sources but have not been able to make it work. The script should run at the scripts directory as working directory and also the terminal that started the script should be kept visible. I have mainly used the «Startup Applications» and different configurations of .desktop files in ~/user/.config/autostart I have tried with running shell files that work on their own as the below:
[Desktop Entry] Type=Application Terminal=true Exec=/home/user/autostart.sh Hidden=false NoDisplay=false X-GNOME-Autostart-enabled=True Name=autostart_shell Comment= #!/usr/bin/env bash sleep 10 cd /home/user/environment bin/python3 main.py bash #!/usr/bin/env bash sleep 10 cd /home/user/environment source bin/activate python3 main.py bash However the environment never gets activated. I have also tried other .desktop-configurations as below without success
[Desktop Entry] Type=Application Path=/home/user/env/ Terminal=true Exec=gnome-terminal --command 'bash -ec "sleep 10;cd /home/user/env;source bin/activate;python3 main.py;bash"' Hidden=false NoDisplay=false X-GNOME-Autostart-enabled=true I’ve spent most of the day on this without any success, does anyone have any ideas? UPDATE Ok, after some more work the problem is related to activating the virtual environment. I’m using the «Startup Applications» to run a shell script. I have tried both the gnome-terminal and xterm with the same result. Below is the command in the *.desktop jobs
gnome-terminal --command '/home/user/folder/startup.sh' xterm /home/user/folder/startup.sh #!/bin/bash # Give it some time to make sure everything is loaded sleep 5 # Logging to make sure it is run TIMESTAMP=`date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"` echo "$TIMESTAMP - program was run " >> /home/user/folder/log.txt # Switching working directory cd /home/user/folder # Alternative 1 # Run python script with virtual envirnments python binary /home/user/folder/bin/python3 /home/user/folder/main.py # Alternative 2 # Activate environment and then run source /home/user/folder/bin/activate python3 /home/user/folder/main.py # Keep the terminal open bash On boot and login the terminal is launched but a python error is displayed about a missing module. If the shell script is run standalone it works without a problem, but launched from the «Startup applications» it is not. This is nagging me so hard, is it really not possible to start a terminal in a python virtual environment?
How to Run Python Script at Startup in Ubuntu
The reputation of Python as a programming language speaks for itself. This programming language is attributed as general-purpose, high level, and interpreted.
Most Linux users are in love with the Python programming language due to its code readability which makes it easy to follow and master even for a beginner in the programming world.
Some advantages of Python Programming language are listed below:
- Open-source and community development support.
- Rich in third-party modules.
- User-friendly data structures.
- Dynamically typed programming language.
- Interpreted language.
- Highly efficient.
- Portable and interactive.
- Extensive libraries support.
The above-mentioned features make Python ideal for projects related to software development (desktop, web, gaming, scientific, image processing, and graphic design applications), operating systems, database access, prototyping, and language development.
This article will address the use of Python as a scripting language in an operating system environment (Ubuntu).
Prerequisites
Ensure you meet the following requirements:
- You are a sudoer/root user on a Linux operating system distribution.
- You can comfortably interact with the Linux command-line environment, interpret, and execute its associated commands.
- You have the latest version of Python installed on Ubuntu.
Confirm that you have Python installed by running the command:
$ python3 --version Python 3.8.10
Running a Python Script at Startup in Ubuntu
The following steps will help us achieve the main objective of this article.
Step 1: Create Your Python Script
Create your Python script if it does not already exist. For this article guide purpose, we will create and use the following Python script.
Add the following Python script.
from os.path import expanduser import datetime file = open(expanduser("~") + '/Desktop/i_was_created.txt', 'w') file.write("This LinuxShellTips Tutorial Actually worked!\n" + str(datetime.datetime.now())) file.close() Upon rebooting our Ubuntu system, the above Python script should be able to create a file called i_was_created.txt on the Ubuntu Desktop (Desktop). Inside this file, we should find the text This LinuxShellTips Tutorial Actually worked! together with the date and time of its creation.
Next, move the Python Script to a directory where it can be executed with root user privileges upon system restart. One such viable directory, in this case, is /bin.
Let us move the script using the mv command.
$ sudo mv python_test_code.py /bin
Now create a cron job scheduler that will periodically handle the execution of the above-created Python script (In this case during system startup).
At the bottom of this file, add the line:
@reboot python3 /bin/python_test_code.py &
Save and close the file and then confirm the creation of the cron job schedule:
The @reboot portion of the above line tells the cron job scheduler to execute the script at system startup. The & parameter informs the cron job scheduler to execute the Python script in the background so as not to interfere with normal system startup.
We are now ready to reboot our system
Let us check if our file was created:
$ cat ~/Desktop/i_was_created.txt && echo ''
The existence of the above file confirms the Python script was successfully executed at the Ubuntu system startup.
Как поставить на автозапуск python скрипт в linux?
Есть запускаю просто из под рута в консоле — всё срабатывает ок. Приложение запускается, всё отрабатывает ок.
Но не понимаю как это поставить на автозапуск (провайдер зачастил ребутать серверы).
Скрипт сервиса:
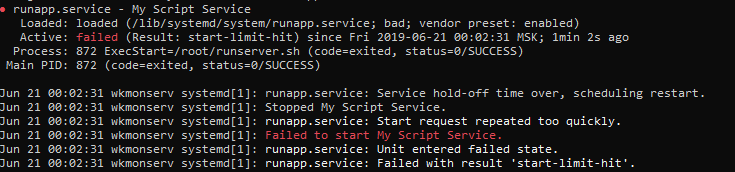
[Unit] Description=My Script Service After=default.target [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/root/runserver.sh Restart=always User=root [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetЛежит в /lib/systemd/system/runapp.service
Скрин статуса:
Заодно подскажите куда как прописать правила iptables так же при старте 🙂
Что читаю и пытаюсь повторить — не работает :\
1. Вам влом прочитать документацию на инструменты используемые вами
— docs.gunicorn.org/en/stable/deploy.html
2. Вам влом в гугле вбить запрос на поиск методов деплоя используемых вами инструментов
— https://bartsimons.me/gunicorn-as-a-systemd-service/
3. Вам влом изучать операционную систему и её инструменты
— https://habr.com/ru/company/southbridge/blog/255845/
4. Выкиньте нафиг свой скрипт, systemd супервизор и он не занимается запуском скриптиков, а если уж очень хочется то не забывайте про «переменные среды».
Но зато не влом прийти и написать много букав на тостере и при этом даже не удосужились указать операционную систему, конкретную а не общее Linux коих 100500 дистров и у многих свои приколы.
[Unit] Description=My Script Service [Service] WorkingDirectory=/home/dev/myapp ExecStart=source venv/bin/activate && gunicorn -c gunicorn_config.py run_app:app Restart=always RestartSec=30 #перезагрузка сервиса, если вдруг упадет. StandardOutput=syslog StandardError=syslog SyslogIdentifier=my-python-app #Environment=NODE_ENV=production PORT=3080 (это для nodejs, но можете тоже поиграть, если надо). [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetПопробуйте разместить в /etc/systemd/
iptables на разных осях по разному. Создаете скрипт типа:
#! /bin/sh iptables -F iptables -X iptables -t nat -F iptables -t nat -X iptables -t mangle -F iptables -t mangle -X iptables -t raw -F iptables -t raw -X iptables -t security -F iptables -t security -X iptables -P INPUT DROP iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPTПо iptables нашел такое решение https://help.ubuntu.com/community/IptablesHowTo#Tips
+ наверно так же на сервис повешу, спасибо.
У меня VPS ubuntu 16.04
Еще помогло это https://habr.com/ru/post/351566/, у меня фласк, но суть так же
+ там есть очень важный момент — в конфиге гуникорна не должен стоять параметр daemon=True
Войдите, чтобы написать ответ
Экспорт почты из Exchange Online (office365)?
.py script to run at the startup [duplicate]
Use python3 path/to/file.py instead – doesn’t just running it as an autostart application in the settings suffice?
hey @dessert the thing is rc.local is gone when 17.04 came out. But answer is much appreciated, I will give it a try that way.
2 Answers 2
Not using 17.04, but under 16.04 there is a «Startup and Shutdown» item in «System Settings». There is an «Autostart» item under there that allows you to specify scripts or programs that you want to run at startup.
Hey @George I kept it as simple as possible. I use ubuntu 17.04 terminal, I want to do something that will execute this two command in the startup.
You can use a cronjob. Edit your cronjobs with crontab -e , and add the script to run
@reboot /home/user/script.sh as an example
It is best to use a full path to your script
Does the script do what you want when you simply run it from your terminal? You should make sure the script is executable: chmod +x /home/user/script.sh Then try running /home/user/script.sh from the terminal and see if you get the desired result.
This will not work if invoking your script from the command line does not do what you want. Even if you are not in Folder . If you haven’t already, add the interpreter you are using at the top of the script. For example #!/usr/bin/python3 . Or wherever you have python3. Use chomd +x to make the script executable. Then try running your script. Just /home/usr/script.py without python3 at the beginning. If the script MUST run from the directory Folder, you can try changing it to use full paths as well