- Info articles 8 html
- Синтаксис
- Атрибуты
- Закрывающий тег
- Браузеры
- Статьи по теме
- Статьи по теме
- Типы тегов
- HTML Introduction
- What is HTML?
- A Simple HTML Document
- Example
- My First Heading
- Example Explained
- What is an HTML Element?
- Web Browsers
- HTML Page Structure
- This is a heading
- HTML History
- Семантическая структура страницы
- Lorem ipsum
- Комментарии
- Неплохо
- Бред
- Непонятно
- Info articles 8 html
- Кратко
- Пример
- Кратко
- Пример
- Как пишется
- Как понять
- Подсказки
- или ?
- : The Article Contents element
- Try it
- Attributes
- Usage notes
- Examples
- Result
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
Info articles 8 html
Тег задает содержание сайта вроде новости, статьи, записи блога, форума или др.
Синтаксис
Атрибуты
Закрывающий тег
Следы невиданных зверей
История о том, как возле столовой появились загадочные розовые следы с шестью пальцами, и почему это случилось. Браузеры
Internet Explorer до версии 8.0 включительно игнорирует тег , но отображает его содержимое. Также в этом браузере любые стили не применяются к селектору article .
Firefox полностью поддерживает этот тег начиная с версии 4.0, но версии 3.0 и старше также корректно отображают содержимое тега.
Статьи по теме
Статьи по теме
Не выкладывайте свой код напрямую в комментариях, он отображается некорректно. Воспользуйтесь сервисом cssdeck.com или jsfiddle.net, сохраните код и в комментариях дайте на него ссылку. Так и результат сразу увидят.
Типы тегов
HTML5
Блочные элементы
Строчные элементы
Универсальные элементы
Нестандартные теги
Осуждаемые теги
Видео
Документ
Звук
Изображения
Объекты
Скрипты
Списки
Ссылки
Таблицы
Текст
Форматирование
Формы
Фреймы
HTML Introduction
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
What is HTML?
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML consists of a series of elements
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as «this is a heading», «this is a paragraph», «this is a link», etc.
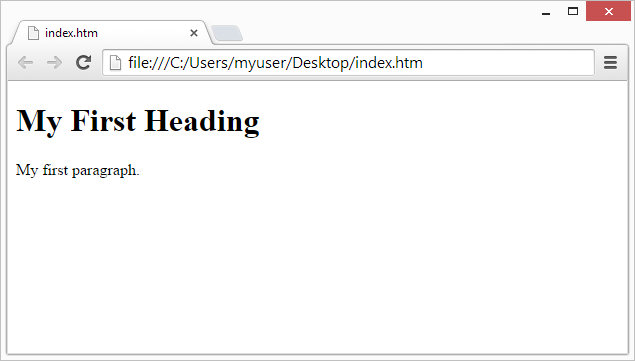
A Simple HTML Document
Example
My First Heading
My first paragraph.
Example Explained
- The declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document
- The element is the root element of an HTML page
- The element contains meta information about the HTML page
- The element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab)
- The element defines the document’s body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
- The element defines a large heading
- The
element defines a paragraph
What is an HTML Element?
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:
The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
Note: Some HTML elements have no content (like the
element). These elements are called empty elements. Empty elements do not have an end tag!
Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
HTML Page Structure
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
This is a heading
This is another paragraph.
Note: The content inside the section will be displayed in a browser. The content inside the element will be shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab.
HTML History
Since the early days of the World Wide Web, there have been many versions of HTML:
| Year | Version |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invented www |
| 1991 | Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML |
| 1993 | Dave Raggett drafted HTML+ |
| 1995 | HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0 |
| 1997 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2 |
| 1999 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01 |
| 2000 | W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0 |
| 2008 | WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft |
| 2012 | WHATWG HTML5 Living Standard |
| 2014 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5 |
| 2016 | W3C Candidate Recommendation: HTML 5.1 |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.1 2nd Edition |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.2 |
This tutorial follows the latest HTML5 standard.
Семантическая структура страницы
Элемент article представляет целостный блок информации на странице, который может рассматриваться отдельно и использоваться независимо от других блоков. Например, это может быть пост на форуме или статья в блоге, онлайн-журнале, комментарий пользователя.
Один элемент article может включать несколько элементов article. Например, мы можем заключить в элемент article всю статью в блоге, и этот элемент будет содержать другие элементы article, которые представляют комментарии к этой статье в блоге. То есть статья в блоге может рассматриваться нами как отдельная семантическая единица, и в то же время комментарии также могут рассматривать отдельно вне зависимости от другого содержимого.
Использование article на примере статьи из блога с комментариями:
Lorem ipsum
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat .Комментарии
Неплохо
Норм статья
Бред
Мне не понравилось.
Непонятно
О чем вообще все это?
Здесь вся статья может быть помещена в элемент article, и в то же время каждый отдельный комментарий также представляет отдельный элемент article.
При использовании article надо учитывать, что каждый элемент article должен быть идентифицирован с помощью включения в него заголовка h1-h6.
Info articles 8 html
Тег для создания самостоятельных единиц контента: от карточек до комментов. Не для статей!
Время чтения: меньше 5 мин
Кратко
Скопировать ссылку «Кратко» Скопировано
Тег обозначает законченный и самодостаточный раздел документа, описывающий какую-то сущность: товар, карточку пользователя, рекламный баннер, виджет.
Пример
Скопировать ссылку «Пример» Скопировано
Тег
<article>, и с чем его едятКратко
Тег<article>обозначает законченный и самодостаточный раздел документа, описывающий какую-то сущность: статью, товар, карточку пользователя и т. д.Пример
Рекурсия! 💥article> h1>Тег code><article>code>, и с чем его едятh1> h2>Краткоh2> p> Тег code><article>code> обозначает законченный и самодостаточный раздел документа, описывающий какую-то сущность: статью, товар, карточку пользователя и т. д. p> h2>Примерh2> pre> code>Рекурсия! 💥code> pre> article>
Как пишется
Скопировать ссылку «Как пишется» Скопировано
article> article> Как понять
Скопировать ссылку "Как понять" Скопировано
Тег семантически «помечает», что его содержимое — это какая-то одна конкретная сущность. Никакого поведенческого или иного оформления это не даёт, визуально выглядит как блочный -элемент.
Подсказки
Скопировать ссылку "Подсказки" Скопировано
или ?
Скопировать ссылку "article или section?" Скопировано
Например, если мы верстаем книгу с главой «Бран», повествующей «о 7-летнем юноше, сыне лорда Винтерфелла», то это скорее всего , так как в книге наверняка есть и другие разделы (главы, не обязательно только об этом персонаже).
С другой стороны, можно представить твит, виджет с погодой или рекламный баннер — каждый из этих блоков будет уже , потому что каждый из них полноценен и самодостаточен по своему содержанию.
: The Article Contents element
The HTML element represents a self-contained composition in a document, page, application, or site, which is intended to be independently distributable or reusable (e.g., in syndication). Examples include: a forum post, a magazine or newspaper article, or a blog entry, a product card, a user-submitted comment, an interactive widget or gadget, or any other independent item of content.
Try it
A given document can have multiple articles in it; for example, on a blog that shows the text of each article one after another as the reader scrolls, each post would be contained in an element, possibly with one or more s within.
| Content categories | Flow content, sectioning content, palpable content |
|---|---|
| Permitted content | Flow content. |
| Tag omission | None, both the starting and ending tag are mandatory. |
| Permitted parents | Any element that accepts flow content. Note that an element must not be a descendant of an element. |
| Implicit ARIA role | article |
| Permitted ARIA roles | application , document , feed , main , none , presentation , region |
| DOM interface | HTMLElement |
Attributes
This element only includes the global attributes.
Usage notes
- Each should be identified, typically by including a heading ( - element) as a child of the element.
- When an element is nested, the inner element represents an article related to the outer element. For example, the comments of a blog post can be elements nested in the representing the blog post.
- Author information of an element can be provided through the element, but it doesn't apply to nested elements.
- The publication date and time of an element can be described using the datetime attribute of a element.
Examples
article class="film_review"> h2>Jurassic Parkh2> section class="main_review"> h3>Reviewh3> p>Dinos were great!p> section> section class="user_reviews"> h3>User reviewsh3> article class="user_review"> h4>Too scary!h4> p>Way too scary for me.p> footer> p> Posted on time datetime="2015-05-16 19:00">May 16time> by Lisa. p> footer> article> article class="user_review"> h4>Love the dinos!h4> p>I agree, dinos are my favorite.p> footer> p> Posted on time datetime="2015-05-17 19:00">May 17time> by Tom. p> footer> article> section> footer> p> Posted on time datetime="2015-05-15 19:00">May 15time> by Staff. p> footer> article>
Result
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser