- Pandas : How to create an empty DataFrame and append rows & columns to it in python
- Create an empty DataFrame with only column names but no rows
- Frequently Asked:
- Append rows to empty DataFrame
- Create an complete empty DataFrame without any column name or indices
- Appends columns to an empty DataFrame
- Create an empty Dataframe with column names & row indices but no data
- Add rows to an empty dataframe at existing index
- Related posts:
- Append Columns to pandas DataFrame in Loop in Python (Example)
- Example Data & Libraries
- Example: Append Columns to pandas DataFrame within for Loop
- Video & Further Resources
- Pandas – Append Columns to Dataframe
- Technique 1: Use Join
- Technique 2: Use Concat
- Conclusion
- Ajitesh Kumar
Pandas : How to create an empty DataFrame and append rows & columns to it in python
In this article we will discuss different ways to create an empty DataFrame and then fill data in it later by either adding rows or columns.
Suppose we want to create an empty DataFrame first and then append data into it at later stages. Let’s see how to do that,
Import python’s pandas module like this,
Create an empty DataFrame with only column names but no rows
Suppose we know the column names of our DataFrame but we don’t have any data as of now. So we will create an empty DataFrame with only column names like this,
Frequently Asked:
# Creating an empty Dataframe with column names only dfObj = pd.DataFrame(columns=['User_ID', 'UserName', 'Action']) print("Empty Dataframe ", dfObj, sep='\n') Contents of the created empty DataFrame will be,
Columns: [User_ID, UserName, Action] Index: []
Dataframe class provides a constructor to create Dataframe object by passing column names , index names & data in argument like this,
def __init__(self, data=None, index=None, columns=None, dtype=None,
To create an empty dataframe object we passed columns argument only and for index & data default arguments will be used.
Append rows to empty DataFrame
As we have created an empty DataFrame, so let’s see how to add rows to it,
# Append rows in Empty Dataframe by adding dictionaries dfObj = dfObj.append(, ignore_index=True) dfObj = dfObj.append(, ignore_index=True) dfObj = dfObj.append(, ignore_index=True) print("Dataframe Contens ", dfObj, sep='\n') User_ID UserName Action 0 23 Riti Login 1 24 Aadi Logout 2 25 Jack Login
Three rows were added to the DataFrame.
Create an complete empty DataFrame without any column name or indices
We can create a complete empty dataframe by just calling the Dataframe class constructor without any arguments like this,
# Create an completely empty Dataframe without any column names, indices or data dfObj = pd.DataFrame()
As we have not passed any arguments, so default value of all arguments will be None and it will create an empty dataframe dfObj. It’s contents are as follows,
Now let’s see how to append columns with data to this empty Dataframe,
Appends columns to an empty DataFrame
# Append columns to the Empty DataFrame dfObj['UserName'] = ['Riti', 'Aadi', 'Jack'] dfObj['Name'] = ['Riti', 'Aadi', 'Jack'] dfObj['Name'] = ['Riti', 'Aadi', 'Jack'] print("Dataframe Contents ", dfObj, sep='\n') Dataframe Contens UserName Name 0 Riti Riti 1 Aadi Aadi 2 Jack Jack
Create an empty Dataframe with column names & row indices but no data
It might be possible in some cases that we know the column names & row indices at start but we don’t have data yet. So we will create an empty DataFrame and add data to it at later stages like this,
# Create an empty Dataframe with columns or indices dfObj = pd.DataFrame(columns=['User_ID', 'UserName', 'Action'], index=['a', 'b', 'c']) print("Empty Dataframe", dfObj, sep='\n') Here we passed the columns & index arguments to Dataframe constructor but without data argument. So, it will create an empty dataframe with all data as NaN.
User_ID UserName Action a NaN NaN NaN b NaN NaN NaN c NaN NaN NaN
Add rows to an empty dataframe at existing index
dfObj.loc['a'] = [23, 'Riti', 'Login'] dfObj.loc['b'] = [24, 'Aadi', 'Logout'] dfObj.loc['c'] = [25, 'Jack', 'Login'] print("Dataframe Contents ", dfObj, sep='\n') Dataframe Contents User_ID UserName Action a 23 Riti Login b 24 Aadi Logout c 25 Jack Login
Complete example is as follows:
import pandas as pd def main(): print('*** Create an empty DataFrame with only column names ***') # Creating an empty Dataframe with column names only dfObj = pd.DataFrame(columns=['User_ID', 'UserName', 'Action']) print("Empty Dataframe ", dfObj, sep='\n') print('*** Appends rows to an empty DataFrame using dictionary with default index***') # Append rows in Empty Dataframe by adding dictionaries dfObj = dfObj.append(, ignore_index=True) dfObj = dfObj.append(, ignore_index=True) dfObj = dfObj.append(, ignore_index=True) print("Dataframe Contens ", dfObj, sep='\n') print('*** Create an completely empty DataFrame ***') # Create an completely empty Dataframe without any column names, indices or data dfObj = pd.DataFrame() print("Empty Dataframe", dfObj, sep='\n') print('*** Appends columns to an empty DataFrame ***') # Append columns to the Empty DataFrame dfObj['UserName'] = ['Riti', 'Aadi', 'Jack'] dfObj['Name'] = ['Riti', 'Aadi', 'Jack'] dfObj['Name'] = ['Riti', 'Aadi', 'Jack'] print("Dataframe Contents ", dfObj, sep='\n') print('*** Create an empty DataFrame with column and index names but no Data ***') # Create an empty Dataframe with columns or indices dfObj = pd.DataFrame(columns=['User_ID', 'UserName', 'Action'], index=['a', 'b', 'c']) print("Empty Dataframe", dfObj, sep='\n') print('*** Appends rows to an empty DataFrame on an existing index***') dfObj.loc['a'] = [23, 'Riti', 'Login'] dfObj.loc['b'] = [24, 'Aadi', 'Logout'] dfObj.loc['c'] = [25, 'Jack', 'Login'] print("Dataframe Contents ", dfObj, sep='\n') if __name__ == '__main__': main() *** Create an empty DataFrame with only column names *** Empty Dataframe Empty DataFrame Columns: [User_ID, UserName, Action] Index: [] *** Appends rows to an empty DataFrame using dictionary with default index*** Dataframe Contens User_ID UserName Action 0 23 Riti Login 1 24 Aadi Logout 2 25 Jack Login *** Create an completely empty DataFrame *** Empty Dataframe Empty DataFrame Columns: [] Index: [] *** Appends columns to an empty DataFrame *** Dataframe Contents UserName Name 0 Riti Riti 1 Aadi Aadi 2 Jack Jack *** Create an empty DataFrame with column and index names but no Data *** Empty Dataframe User_ID UserName Action a NaN NaN NaN b NaN NaN NaN c NaN NaN NaN *** Appends rows to an empty DataFrame on an existing index*** Dataframe Contents User_ID UserName Action a 23 Riti Login b 24 Aadi Logout c 25 Jack Login
Related posts:
Append Columns to pandas DataFrame in Loop in Python (Example)
This tutorial demonstrates how to add new columns to a pandas DataFrame within a for loop in Python programming.
The article will contain one example for the addition of new variables to a pandas DataFrame within a for loop. To be more specific, the post is structured as follows:
Let’s dive right into the example…
Example Data & Libraries
We first have to import the pandas library, if we want to use the corresponding functions:
import pandas as pd # Load pandas
In addition, have a look at the following example data:
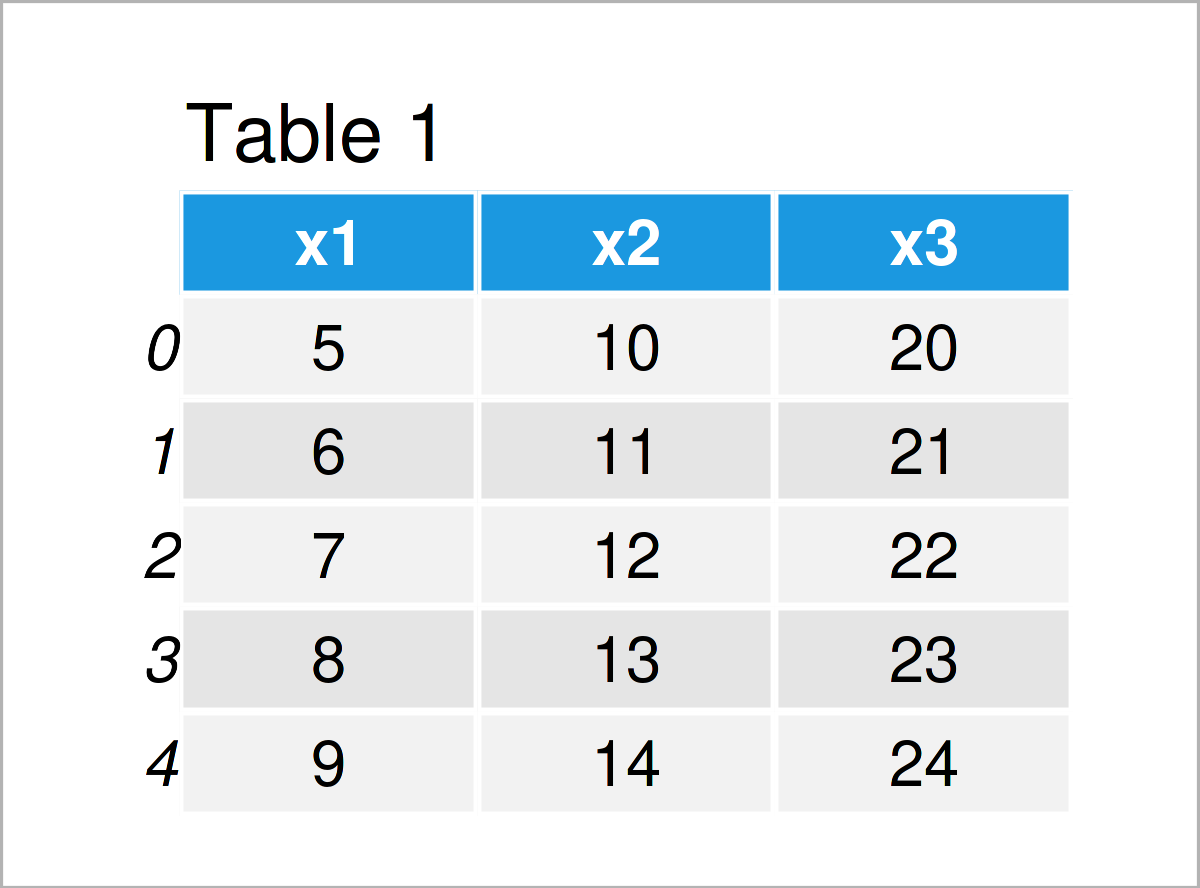
data = pd.DataFrame('x1':range(5, 10), # Create pandas DataFrame 'x2':range(10, 15), 'x3':range(20, 25)>) print(data) # Print pandas DataFrame
Have a look at the table that got returned after executing the previously shown Python programming code. It shows that our example pandas DataFrame is constructed of five data points and three columns.
Example: Append Columns to pandas DataFrame within for Loop
In this example, I’ll illustrate how to use a for loop to append new variables to a pandas DataFrame in Python.
Have a look at the Python syntax below. It shows a for loop that consists of two lines.
The first line specifies that we want to iterate over a range from 1 to 4.
The second line specifies what we want to do in this loop, i.e. in each iteration we want to add a new column containing the iterator i times the value three. The variable name of this new column should be called like the iterator.
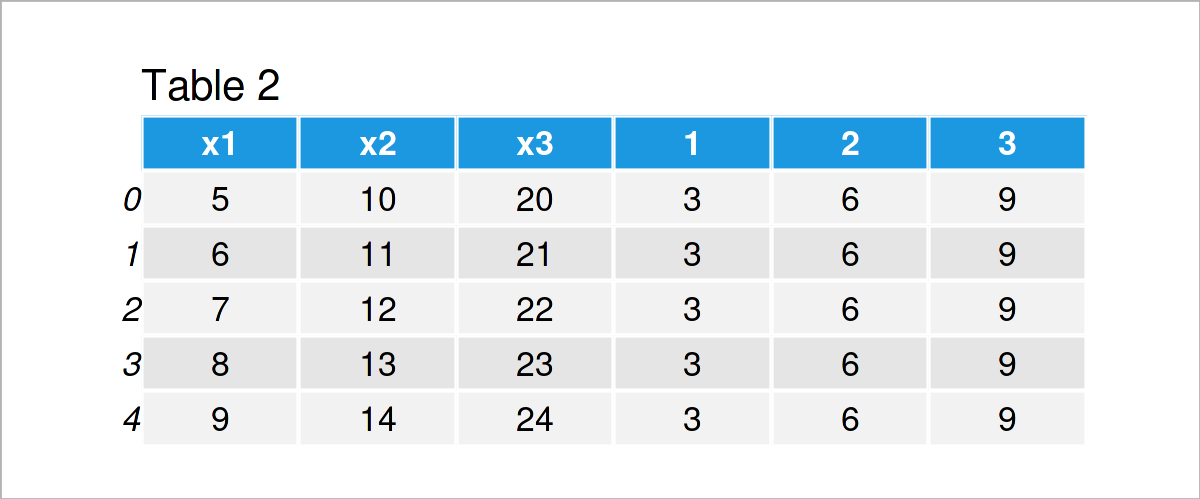
for i in range(1, 4): # Append columns within for loop data[i] = i * 3 print(data) # Print updated DataFrame
Table 2 shows the output of the previous code: We have extended our example data set by three new columns.
Video & Further Resources
I have recently published a video on my YouTube channel, which illustrates the Python programming code of this article. You can find the video below.
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.
If you accept this notice, your choice will be saved and the page will refresh.
Accept YouTube Content
Additionally, you could read the other posts on this homepage. A selection of articles is shown below.
- Append Rows to pandas DataFrame in Loop
- Iterate Over Columns of pandas DataFrame
- Iterate Through Rows of pandas DataFrame
- Combine Two Text Columns of pandas DataFrame in Python
- Sort pandas DataFrame by Multiple Columns in Python
- Count Rows & Columns of pandas DataFrame in Python
- Rename Columns of pandas DataFrame in Python in R
- Append pandas DataFrame in Python
- Append Values to pandas DataFrame in Python
- Introduction to the pandas Library in Python
- The Python Programming Language
This tutorial has shown how to append, combine, and concatenate new variables to a pandas DataFrame within a for loop in Python. If you have any additional questions, please let me know in the comments below. In addition, please subscribe to my email newsletter to receive updates on new posts.
Pandas – Append Columns to Dataframe
In this post, you will learn different techniques to append or add one column or multiple columns to Pandas Dataframe (Python). There are different scenarios where this could come very handy. For example, when there are two or more data frames created using different data sources, and you want to select a specific set of columns from different data frames to create one single data frame, the methods given below can be used to append or add one or more columns to create one single data frame. It will be good to know these methods as it helps in data preprocessing stage of building machine learning models.
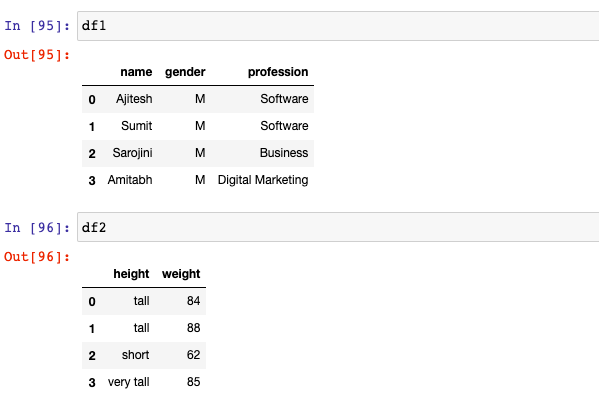
In this post, we will work the following two Pandas data frames. The requirement is to append second data frame (df2) to first dataframe (df1)
import pandas as pd # # Dataframe 1 having 3 columns # df1 = pd.DataFrame([ ['Ajitesh', 'M', 'Software'], ['Sumit', 'M', 'Software'], ['Sarojini', 'M', 'Business'], ['Amitabh', 'M', 'Digital Marketing'] ]) df1.columns = ['name', 'gender', 'profession'] # # Dataframe 2 having 2 columns # df2 = pd.DataFrame([ ['tall', 84], ['tall', 88], ['short', 62], ['very tall', 85] ]) df2.columns = ['height', 'weight']
This is how the above data frames look like.
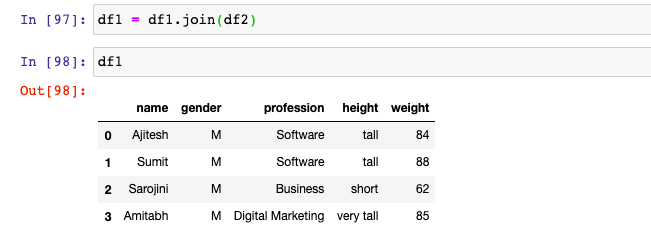
Technique 1: Use Join
Use Dataframe Join method to append one or more columns to existing data frame. Note that columns of df2 is appended to df1. The following code will work:
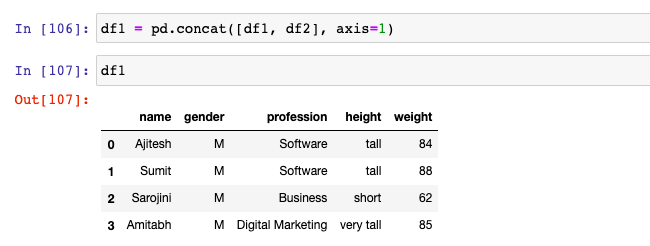
Technique 2: Use Concat
Use Pandas concat method to append one or more columns to existing data frame. The way this is different from join method is that concat method (static method) is invoked on pandas class while join method is invoked on an instance of data frame. Note that columns of df2 is appended to df1. The following code will work:
df1 = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1)
Conclusion
In this post, you learned about how to append or add one column or multiple columns to the Pandas data frame. Here are two commands which can be used:
- Use Dataframe join command to append the columns
- Use Pandas concat command to append the columns
- Both methods can be used to join multiple columns from different data frames and create one data frame.
Ajitesh Kumar
I have been recently working in the area of Data analytics including Data Science and Machine Learning / Deep Learning. I am also passionate about different technologies including programming languages such as Java/JEE, Javascript, Python, R, Julia, etc, and technologies such as Blockchain, mobile computing, cloud-native technologies, application security, cloud computing platforms, big data, etc. For latest updates and blogs, follow us on Twitter. I would love to connect with you on Linkedin. Check out my latest book titled as First Principles Thinking: Building winning products using first principles thinking