- Python dictionary extend – Complete tutorial
- Python dictionary extend
- How to extend a dictionary in Python
- Python dictionary extend vs append
- Python dictionary extend list
- Python extend dictionary class
- Python dictionary extend function
- Python extend dictionary with another
- Python dictionary extend vs update
- Python: How to Add Items to Dictionary
- How to Add an Item to a Dictionary in Python
- Method 1: Using The Assignment Operator
- Method 2: Using update()
- Method 3: Using __setitem__
- Method 4: Using The ** Operator
- Method 5: Checking If A Key Exists
- Method 6: Using A For Loop
- Method 7: Using zip
- How to Update a Python Dictionary
Python dictionary extend – Complete tutorial
In this Python tutorial, we will discuss the Python dictionary extend. Here we will also cover the below examples:
- Python dictionary extend vs append
- Python dictionary extend list
- Python extend dictionary class
- Python dictionary extend function
- Python extend dictionary with another
- Python dictionary extend vs update
Python dictionary extend
- In this programm we will see how to extend a dictionary in Python.
- In Python, the dict.update() will help the user to extend a dictionary with the key-value pair from one dictionary to another.
Let’s take an example and check how to extend a dictionary in Python.
my_dict1 = new_dictionary = my_dict1.update(new_dictionary) print(my_dict1)In the above example first, we initialize two dictionaries ‘my_dict1’ and ‘new_dictionary’ which contain elements in the form of key-value pair.
Now we have to use dict.update() method to extend the dictionary into another one.
Here is the execution of the following give code
How to extend a dictionary in Python
By using the ** operator we can perform this particular task and this method adds the specified dictionary elements to the end of the current dictionary.
Source Code:
This is how to extend a dictionary in Python.
Python dictionary extend vs append
- In Python dictionary, the append() function is used to add elements to the keys in the dictionary. In the dictionary extend() means to concatentates the first dictionary with another dictionary.
- In Python dictionary, the append() function is used to add elements to the keys in the dictionary. In the dictionary extend() means to concatenate the first dictionary with another dictionary.
- In this programm, we will learn about the update() function and check how to add elements in a given dictionary. In a Python dictionary, the update() function is used to update the dictionary with the elements in the form of Key-value pair from another dictionary.
- In Python dictionary, append can be used by list as a list, we can also use “+” operator to append the lists of each key within a dictionary.
Let’s an example and check the combination of update and append() function Python dictionary
student_name = add_new = student_name.update(add_new) print("Update elements",student_name) new_country = new_country['Germany'] = [8] new_country['Germany'].append('France') print("Append elements",new_country)After writing the above code, you will see first we initialize a dictionary that stores key-value pair elements. Here the update() function is used to add the element in the dictionary and call the print statement to display the output.
After that create another dictionary and use the append function to insert the elements in the dictionary.
Here is the execution of the following given code
Python dictionary extend list
- Here we can see how to update the value list in a Python dictionary.
- By using list comprehension method we can update the value list and extract a particular key and then iterate over it’s value in this method.
Source Code:
stud_dictionary = stud_dictionary['student_val'] = [y * 4 for y in stud_dictionary['student_val']] print("Updated dictionary:",stud_dictionary)In the above code, once you will print “stud_dictionary” then the result will display as a “student_val”:[36,8,4]. In this program, the “*” operator is used to update the values from a list. You can check the below screenshot for updating the value list.
Python extend dictionary class
- In this program, we will see how to extend a Python dictionary class whose instances will keep the data contained by their element in the form of key-value pair.
- In this example we can apply the subclasses like dict and use built-in keyword like ‘self’ and ‘super’.
class my_new_dict(dict): def __init__(self, *b, **a): super(my_new_dict,self).__init__(*b, **a) self.itemlist = super(my_new_dict,self).keys() def __setitem__(self, new_k, new_va): set(self.itemlist).add(new_k) super(my_new_dict,self).__setitem__(new_k, new_va) def __iter__(self): return iter(self.itemlist) new_val = my_new_dict(m=4,z=7) print("original dictionary:",new_val) new_val['u']=15 new_val['w']=19 print ("Updated dictionary:",new_val) Note: In this example dict.keys() method does not return a list so we apply the ‘self. item list’ method.
In the above code, once you will print “new_val” then the output will display as a ‘’. In this program, we use the function ‘_init_’ in which we have assign ‘self’ and ‘*args’ as an argument.
Here is the implementation of the following given code
Python dictionary extend function
Note: In the Python dictionary, there is no built-in extend() function which we can apply in a dictionary. So in this case we can apply the update () function and it will help the user to update the dictionary with the elements in the form of key-value pair from another dictionary.
Python extend dictionary with another
- Let us see how to add a dictionary with another dictionary in Python.
- By using the ** operator we can solve this task and this method inserts the specified dictionary elements in the form of key-value pair to the end of the current dictionary.
my_new_org_dict = update_dict = new_val = <**my_new_org_dict, **update_dict>print(new_val) In the above code first, we will initialize a dictionary called ‘my_new_org_dict’ that stores elements and then use another dictionary ‘update_dict’.
Now in this program, we use the operator ‘**’ for appending elements. Here we can see that the dictionary is added to another dictionary.
You can refer to the below screenshot:
Python dictionary extend vs update
- Here we will discuss the difference between the extend and update method in Python.
- In Python, there is no extend() function in the dictionary but we can apply this method in lists and tuples. In Python, the update() function is used to modify the dictionary and by using this method we can concatenate the old dictionary to a new dictionary.
my_new_dict = <'Mongodb':800,'Sql':892,'C++':956>print("NewLanguages",my_new_dict) my_new_dict.update() print("updated language",my_new_dict)Here is the Output of the following given code
In this Python tutorial, we will discuss the Python dictionary extend. Here we will also cover the below examples:
- Python dictionary extend vs append
- Python dictionary extend list
- Python extend dictionary class
- Python dictionary extend function
- Python extend dictionary with another
- Python dictionary extend vs update
Related Posts:
- Python dictionary values to list
- Python dictionary contains
- Iterate through dictionary Python
- Python dictionary comprehension
- Python dictionary find a key by value
- Python dictionary increment value
- Python dictionary of lists
- Python Count Words in File
- Reverse a list in python
- Python convert dictionary to list
- Python dictionary setdefault() method [With Examples]
I am Bijay Kumar, a Microsoft MVP in SharePoint. Apart from SharePoint, I started working on Python, Machine learning, and artificial intelligence for the last 5 years. During this time I got expertise in various Python libraries also like Tkinter, Pandas, NumPy, Turtle, Django, Matplotlib, Tensorflow, Scipy, Scikit-Learn, etc… for various clients in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, etc. Check out my profile.
Python: How to Add Items to Dictionary
Dictionaries are Python’s built-in data types for storing key-value pairs. The dictionary elements are changeable and don’t allow duplicates. In Python 3.7 and higher, dictionary items are ordered. Lower versions of Python treat dictionary elements as unordered.
Depending on the desired result and given data, there are various ways to add items to a dictionary.
This guide shows how to add items to a Python dictionary through examples.
- Python version 3.7 or higher.
- A text editor or IDE to write code.
- A method to run the code, such as a terminal or IDE.
How to Add an Item to a Dictionary in Python
To test out different methods of adding items to a dictionary, create a dictionary with two items. Use the following code:
The methods below show how to add one or multiple items to a Python dictionary.
Note: Adding an item with an existing key replaces the dictionary item with a new value. Make sure to provide unique keys to avoid overwriting data.
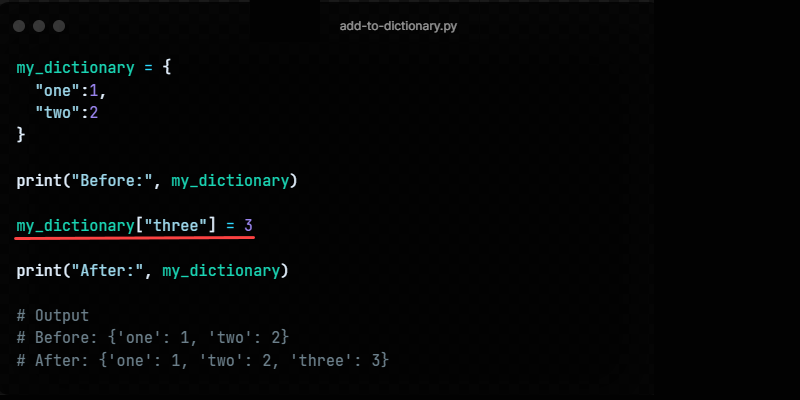
Method 1: Using The Assignment Operator
The assignment operator sets a value to a key using the following syntax:
dictionary_nameAdd to list in dict python = valueThe assignment operator adds a new key-value pair if the key does not exist.
The following code demonstrates how to add an item to a Python dictionary using the assignment operator:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary["tree"] = 3 print("After:", my_dictionary)The code outputs the dictionary contents before and after adding a new item.
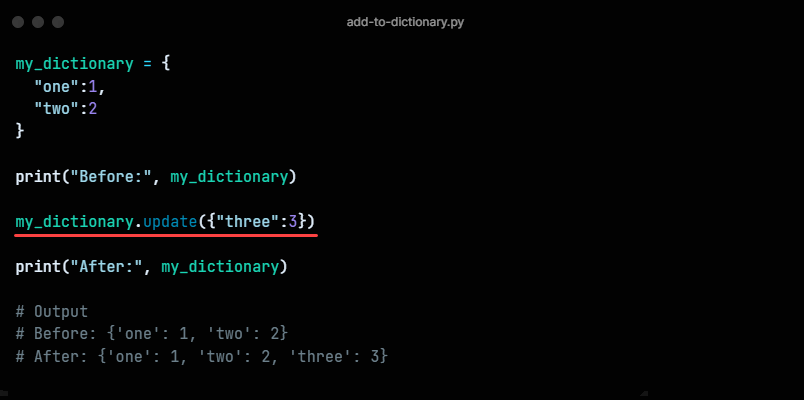
Method 2: Using update()
The update() method updates an existing dictionary with a new dictionary item:
The method accepts one or multiple key-value pairs, which is convenient for adding more than one element.
The example code looks like the following:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary.update() print("After:", my_dictionary)Use this method to add multiple new items or append a dictionary to an existing one.
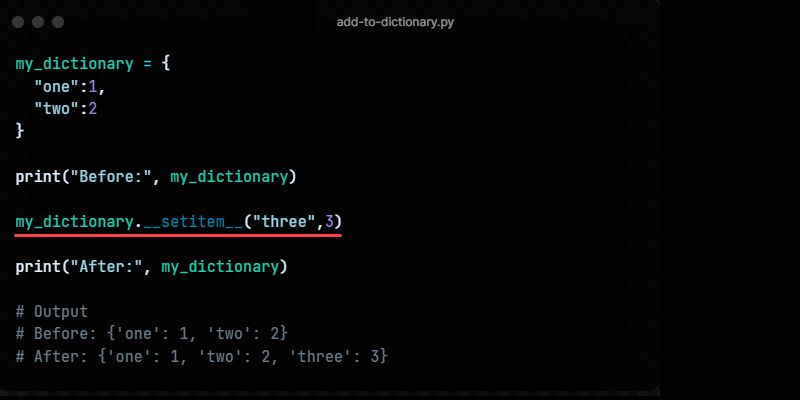
Method 3: Using __setitem__
The __setitem__ method is another way to append a new dictionary item:
dictionary_name.__setitem__(key,value)my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary.__setitem__("three", 3) print("After:", my_dictionary)The method sets the item key as «three» with the value 3 .
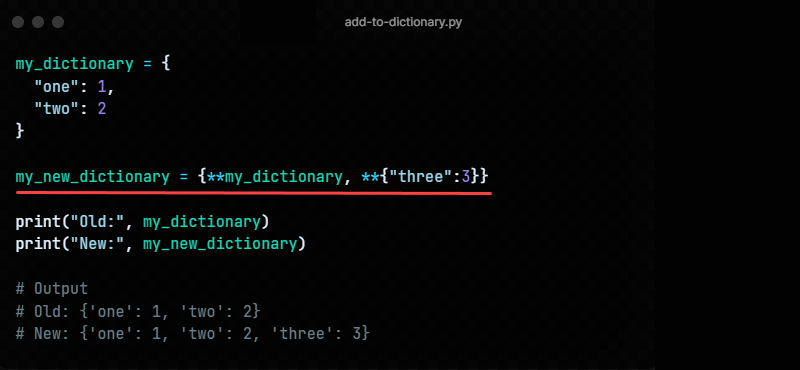
Method 4: Using The ** Operator
The ** operator helps merge an existing dictionary into a new dictionary and adds additional items. The syntax is:
For example, to copy an existing dictionary and append a new item to a new one, see the following code:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >my_new_dictionary = <**my_dictionary, **<"three":3>> print("Old:", my_dictionary) print("New:", my_new_dictionary)The new dictionary contains the added item, preserving the old dictionary values. Use this method to avoid changing existing dictionaries.
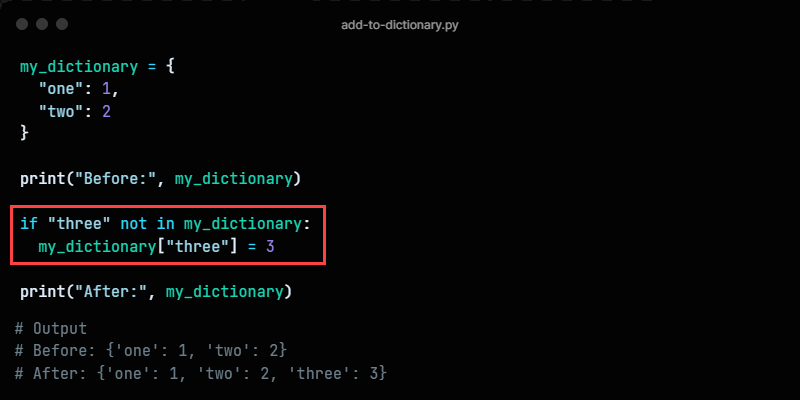
Method 5: Checking If A Key Exists
Use an if statement to check whether a key exists before adding a new item to a dictionary. The example syntax is:
if key not in dictionary_name: dictionary_nameAdd to list in dict python = valuemy_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) if "three" not in my_dictionary: my_dictionary["three"] = 3 print("After:", my_dictionary)The code checks whether a key with the provided name exists before adding the item to the dictionary. If the provided key exists, the existing key value does not update, and the dictionary stays unchanged.
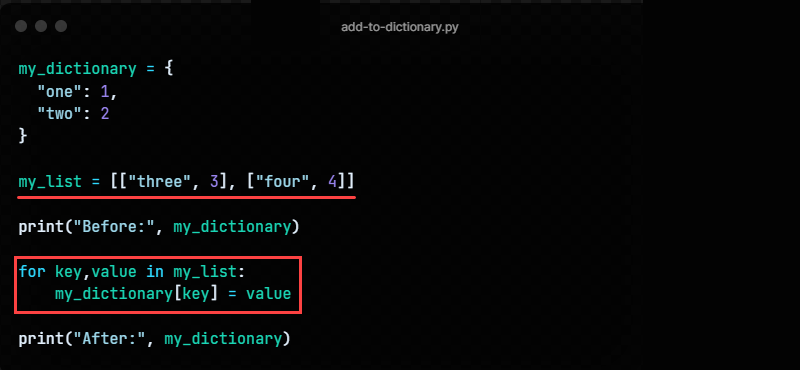
Method 6: Using A For Loop
Add key-value pairs to a nested list and loop through the list to add multiple items to a dictionary. For example:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >my_list = [["three", 3], ["four", 4]] print("Before:", my_dictionary) for key,value in my_list: my_dictionaryAdd to list in dict python = value print("After:", my_dictionary)The for loop goes through the pairs inside the list and adds two new elements.
Note: For loop and a counter are also used as one of the methods to identify the length of a list. Learn more by visiting our guide How to Find the List Length in Python.
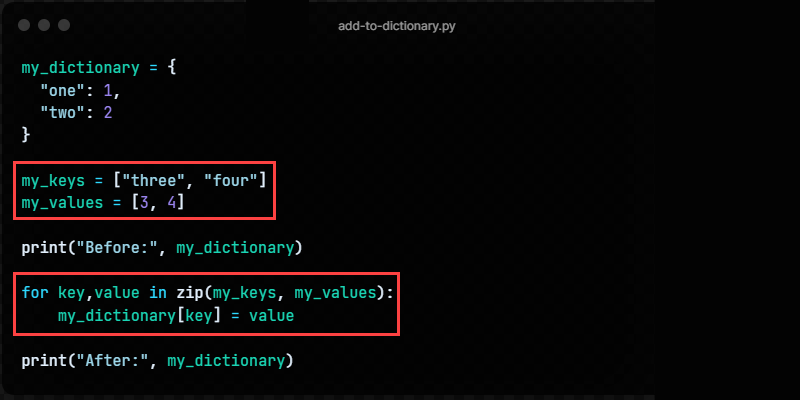
Method 7: Using zip
Use zip to create key-value pairs from two lists. The first list contains keys and the second contains the values.
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >my_keys = ["three", "four"] my_values = [3, 4] print("Before:", my_dictionary) for key,value in zip(my_keys, my_values): my_dictionaryAdd to list in dict python = value print("After:", my_dictionary)The zip function matches elements from two lists by index, creating key-value pairs.
How to Update a Python Dictionary
Update Python dictionary values using the same syntax as adding a new element. Provide the key name of an existing key, for example:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary["one"] = 3 print("After:", my_dictionary)Since Python does not allow duplicate entries in a dictionary, the code updates the value for the provided key and overwrites the existing information.
After going through the examples in this tutorial, you know how to add items to a Python dictionary. All methods provide unique functionalities, so choose a way that best suits your program and situation.
For more Python tutorial refer to our article and find out how to pretty print a JSON file using Python.