- Add Hours to datetime in Python
- datetime in Python
- Ways to add hours to datetime in Python
- Using the datetime.Hour Attribute to Add Hours to datetime in Python
- Further reading:
- Using the datetime.timedelta object to add hours to datetime in Python
- Using the dateutil.Relativedelta Object to Add Hours to datetime in Python
- Using the pandas.Date Offset() Function to Add Hours to datetime in Python
- Add hours to datetime python
- # Add hours to datetime in Python
- # Using the datetime class to create a datetime object
- # Adding hours to the current time
- # Only extracting the time component after adding hours
- # Formatting the time as HH:MM:SS after adding hours
- # Adding hours to a time using datetime.combine()
- # Additional Resources
- How To Add Hours To Datetime In Python
- Add hours to datetime in Python
- Use pandas library
- Use timedelta class
- Use the relativedelta class
- Summary
Add Hours to datetime in Python
This tutorial discusses how to add Hours to datetime in Python.
datetime in Python
To work with date and time values, we can use the datetime module provided in Python. With this module, we can create datetime objects that have different attributes for storing the day, month, year, hour, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds. We can manipulate and modify such objects.
Ways to add hours to datetime in Python
Different methods on how to add hours to datetime in Python are discussed below.
Using the datetime.Hour Attribute to Add Hours to datetime in Python
The datetime constructor is used to create a datetime object in Python. The different attributes for date and time can be specified with this constructor. These objects are not writeable.
There are the hour , minute , second , and microsecond attributes for the time values.
The hour attribute can be used to add hours to datetime in Python.
Further reading:
Add Seconds to Datetime in Python
Add days to date in Python
Using the datetime.timedelta object to add hours to datetime in Python
Directly, we cannot either add or subtract datetime objects in Python. There is another object that acts as an intermediate for such cases.
The datetime.timedelta object represents some type of difference between datetime objects. Such objects can be used to add hours to datetime in Python.
First, we need to create a datetime.timedelta object using the timedelta constructor. We will assign this object with the required hours we want to add using the hours attribute. This object will be then added to a datetime object.
Using the dateutil.Relativedelta Object to Add Hours to datetime in Python
In Python, we can use the dateutil module as an extension to the datetime module by providing more functionalities that can be used with datetime objects.
The dateutil.relativedelta object is similar to the previously discussed timedelta object. It is used to represent some time intervals. The main difference lies in the parameters between the two objects. The relativedelta object accepts a wide range of parameters for date values, something which is not present in the timedelta object.
The relativedelta object can be used to add hours to datetime in Python.
See the following example.
In the above example, we create a relativedelta object and specify the hours we want to add using the hours attribute. This object is added to a given datetime object.
Using the pandas.Date Offset() Function to Add Hours to datetime in Python
The pandas module is used to create and work with DataFrame objects that represent data in rows and columns. Many times these DataFrames encounter date and time values.
That is why the module is equipped with functionalities to manipulate and work with such values. The DateOffset() function adds hours to datetime in Python.
This function is used to add time intervals to given values. We can use the hours attribute to specify the number of hours to be added and use it with the datetime object.
Add hours to datetime python
Last updated: Feb 19, 2023
Reading time · 3 min
# Add hours to datetime in Python
Use the timedelta() class from the datetime module to add hours to datetime, e.g. result = dt + timedelta(hours=10) .
The timedelta class can be passed a hours argument and adds the specified number of hours to the datetime.
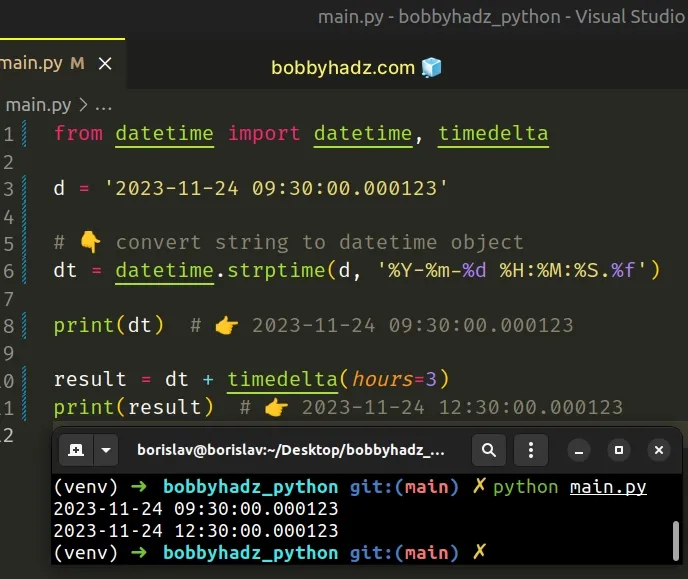
Copied!from datetime import datetime, timedelta d = '2023-11-24 09:30:00.000123' # 👇️ convert string to datetime object dt = datetime.strptime(d, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f') print(dt) # 👉️ 2023-11-24 09:30:00.000123 result = dt + timedelta(hours=3) print(result) # 👉️ 2023-11-24 12:30:00.000123
Make sure to import the datetime and timedelta classes from the datetime module.
The example creates a datetime object from a datetime string and adds hours to it.
Copied!from datetime import datetime, timedelta d = '2023-11-24 09:30:00.000123' # 👇️ convert string to datetime object dt = datetime.strptime(d, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f') print(dt) # 👉️ 2023-11-24 09:30:00.000123 result_1 = dt + timedelta(hours=3) print(result_1) # 👉️ 2023-11-24 12:30:00.000123
The datetime.strptime() method returns a datetime object that corresponds to the provided date string, parsed according to the format.
If you have a date string that is formatted in a different way, use this table of the docs to look up the format codes you should pass as the second argument to the strptime() method.
# Using the datetime class to create a datetime object
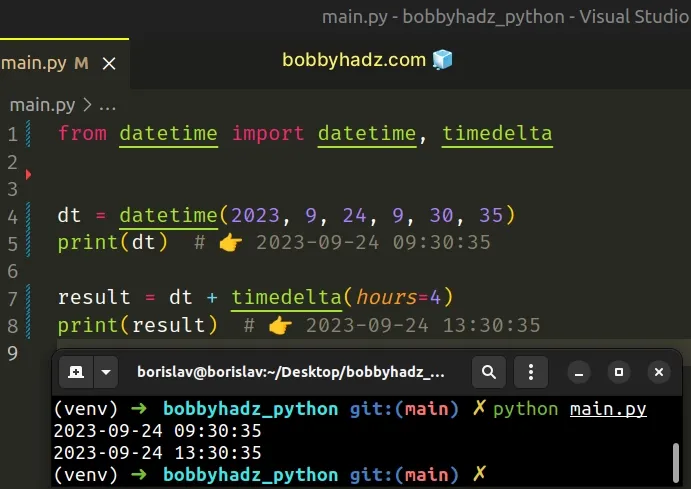
The following example uses the datetime class to create a datetime object and the timedelta class to add hours to it.
Copied!from datetime import datetime, timedelta dt = datetime(2023, 9, 24, 9, 30, 35) print(dt) # 👉️ 2023-09-24 09:30:35 result = dt + timedelta(hours=4) print(result) # 👉️ 2023-09-24 13:30:35
We passed values for the year , month , day , hour , minute and seconds arguments.
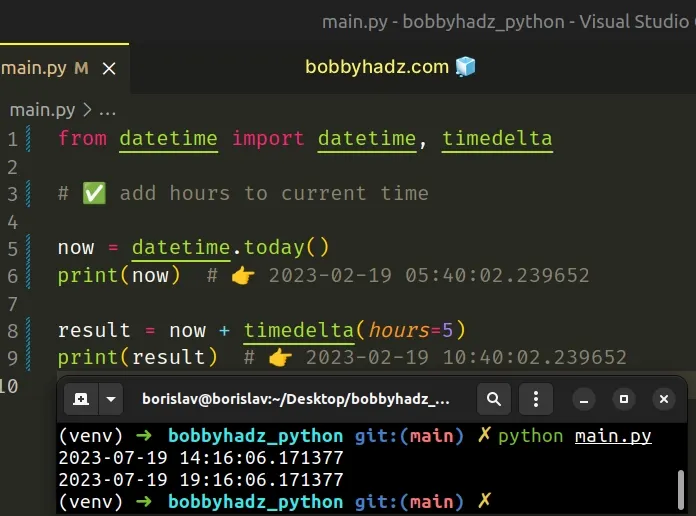
# Adding hours to the current time
If you need to add hours to the current time, use the datetime.today() method to get a datetime object that stores the current time.
Copied!from datetime import datetime, timedelta # ✅ add hours to current time now = datetime.today() print(now) # 👉️ 2023-02-19 05:40:02.239652 result = now + timedelta(hours=5) print(result) # 👉️ 2023-02-19 10:40:02.239652
The datetime.today() method returns the current local datetime.
We need to use a datetime object because it automatically rolls over the days, months and years if necessary.
This wouldn’t be possible if we only had the time component. For example, 11:59:30PM + 2 hours would raise an exception.
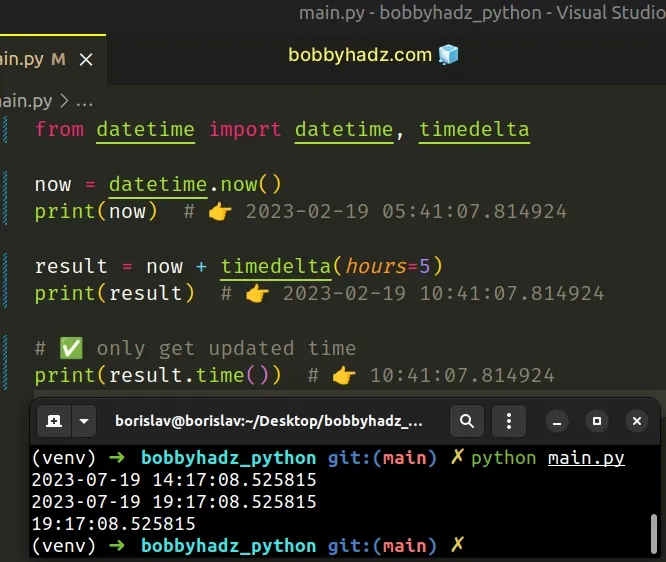
# Only extracting the time component after adding hours
If you only need to extract the time after the operation, call the time() method on the datetime object.
Copied!from datetime import datetime, timedelta now = datetime.now() print(now) # 👉️ 2023-02-19 05:41:07.814924 result = now + timedelta(hours=5) print(result) # 👉️ 2023-02-19 10:41:07.814924 # ✅ only get updated time print(result.time()) # 👉️ 10:41:07.814924
The datetime.time method returns a time object with the same hour, minute, second and millisecond.
# Formatting the time as HH:MM:SS after adding hours
If you need to get the time formatted as HH:MM:SS , use a formatted string literal.
Copied!from datetime import datetime, timedelta now = datetime.now() print(now) # 👉️ 2023-02-19 05:41:40.114944 result = now + timedelta(hours=3) print(result) # 👉️ 2023-02-19 08:41:40.114944 print(result.time()) # 👉️ 08:41:40.114944 # 👇️ format as HH:MM:SS print(f'result:%H:%M:%S>') # 👉️ 08:41:40
Formatted string literals (f-strings) let us include expressions inside of a string by prefixing the string with f .
Make sure to wrap expressions in curly braces — .
Formatted string literals also enable us to use the format specification mini-language in expression blocks.
# Adding hours to a time using datetime.combine()
If you only have the time component, use the datetime.combine method to combine the time with the current (or some other) date and get a datetime object.
Copied!from datetime import datetime, date, timedelta, time t = time(6, 25) print(t) # 👉️ 06:25:00 result = datetime.combine(date.today(), t) + timedelta(hours=6) print(result) # 👉️ 2023-02-19 12:25:00 only_t = result.time() print(only_t) # 👉️ 12:25:00
The datetime.combine method takes a date and time as arguments and returns a new datetime object by combining them.
Once we get a datetime object, we can use the timedelta class to add hours to it.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How To Add Hours To Datetime In Python
To add hours to datetime in Python, you can use the pandas library or timedelta class. Let follow the article to better understand.
Add hours to datetime in Python
In Python, datetime module determines the date and time with the timestamps.
import datetime timeNow = datetime.datetime.now() print(timeNow)
To add hours to datetime, we have the following ways:
Use pandas library
Pandas is a library in Python that provides powerful and flexible data structures and networks. The Pandas library provides a DateOffset class to store time and interval information. It is also used with the datetime module to add N hours to the datetime.
import pandas as pd import datetime timeNow = datetime.datetime.now() print(timeNow ) n = 10 # Add 10 hours to the datetime object timeAfterAdding = timeNow + pd.DateOffset(hours=n) print('Time after adding (10 hours after given time ): ', timeAfterAdding) 2022-10-06 04:48:21.228201 Time after adding (10 hours after given time ): 2022-10-06 14:48:21.228201Use timedelta class
Python has a datetime module that works with and handles dates and timestamps. In that datetime module there are classes like datetime.date , datetime.time , datetime.datetime and datetime.delta . To add N hours from the current datatime I will use datetime.timedelta class.
import datetime from datetime import timedelta timeNow = datetime.datetime.now() print(timeNow ) n = 10 # Add 10 hours to the datetime object timeAfterAdding = timeNow + timedelta(hours=n) print('Time after adding (10 hours after given time ): ', timeAfterAdding) 2022-10-06 05:02:44.414433 Time after adding (10 hours after given time ): 2022-10-06 15:02:44.414433Use the relativedelta class
The dateutil module in Python provides a relativedelta class that you can use to add N hours from the current time period.
import datetime from dateutil.relativedelta import relativedelta timeNow = datetime.datetime.now() print(timeNow) n = 10 # Add 10 hours to the datetime object timeAfterAdding= timeNow + relativedelta(hours=n) print('Time after adding (10 hours after given time ): ', timeAfterAdding) 2022-10-06 05:10:32.017016 Time after adding (10 hours after given time ): 2022-10-06 15:10:32.017016Summary
If you have any questions about how to add hours to datetime in Python, leave a comment below. I will support your questions. Thank you for reading!
Maybe you are interested:
My name is Jason Wilson, you can call me Jason. My major is information technology, and I am proficient in C++, Python, and Java. I hope my writings are useful to you while you study programming languages.
Name of the university: HHAU
Major: IT
Programming Languages: C++, Python, Java